Physicochemical Evaluation of Streptomycin Sulphate using Simple and Newly Developed Spectrophotometric Methods
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
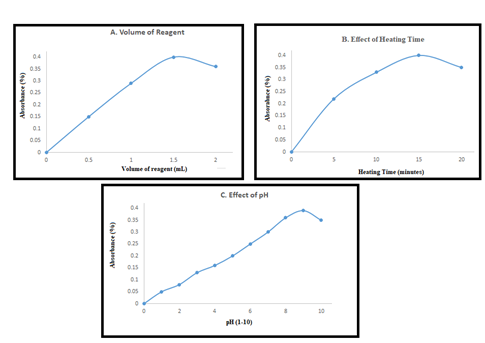
Streptomycin sulphate (STP), an antibiotic that belongs to the aminoglycoside class, works by blocking the protein synthesis of the bacteria. This research presents a simple, fast, and cost-effective method for the analysis of the physicochemical parameters of STP used by three brands. The current study was conducted in two stages. In the first stage, physical properties such as color, pH, and weight variations of brands containing STP were evaluated using simple aesthetic procedures. In the second stage, chemical analysis was carried out using derivatization approach, followed by analysis with spectrophotometer. The derivatization of STP was carried out using vanillin as derivatizing agent. Beer’s law was followed in the range of 10-50 µg/ml, while calibration curve was obtained in the same range with R2value of 0.9993, which shows the linearity of the method. The analysis was carried out using the recovery method. There was 99-101% recovery of the drug using the new method with relative standard deviation ranging between 0.19-0.22%. The results showed that the new method is accurate and precise.
Downloads
References
Arshad H, Waseem H, Khaliq R. Simple and rapid method on high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for estimation of streptomycin sulphate. J World Appl Sci. 2012;19(5):645–649.
Jian W, James DM, Jack FK. Chemical Analysis of Antibiotics Residues in Food. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2012.
Finberg RW, Moellering RC, Tally FP, Craig WA, Pankey GA, Dellinger EP. The importance of bactericidal drugs: future directions in infectious disease. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39(9):1314–1320. https://doi.org/10.1086/425009
Munita JM, Arias CA. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. In: Kudva IT, Cornick NA, Plummer PJ, et al. eds. Virulence Mechanisms of Bacterial Pathogens. Wiley Publishers; 2016:481–511. https://doi.org/10.1128/9781555819286.ch17
Bharadwaj A, Rastogi A, Pandey S, Gupta S, Sohal JS. Multidrug-resistant bacteria: their mechanism of action and prophylaxis. BioMed Res Int. 2022;2022:e5419874. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5419874
Mingeot-Leclercq M-P, Glupczynski Y, Tulkens PM. Aminoglycosides: activity and resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999;43(4):727–737. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.43.4.727
Krause KM, Serio AW, Kane TR, Connolly LE. Aminoglycosides: an overview. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016;6(6):ea027029. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a027029
Durante-Mangoni E, Grammatikos A, Utili R, Falagas ME. Do we still need the aminoglycosides? Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009;33(3):201–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2008.09.001
British Pharmacopoeia. Her Majesty's Stationery Office. 1998.
Hanes SD, Herring VL. Gentamicin enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for microdialysis samples. Ther Drug Monit. 2001;23(6):689–693.
Murali P, Jos H, Ann VS, Erwin A. LC-MS of streptomycin following desalting of a nonvolatile mobile phase and pH gradient. J Sep Sci. 2009;32(20):3418–3424. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200900238
Bagade SB. Sanjay KP. Spectrophotometric estimation of torsemide in tablet dosage form using chemical derivatization technique. Int J Pharm Qual Assur. 2010;2(1):52–55.
Rowe WF. Chemical methods in firearms analysis. In: Siegel JA, ed. Forensic Chemistry: Fundamentals and Applications. Wiley Publishers; 2015:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118897768.ch10
Mitic SS, Miletic GZ, Kostic DA, Rasic ID. A spectrophotometric study of streptomycin effect on the clinical urea determination. Chin J Chem. 2011;29(1):135–142. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.201190041
Omar MA, Nagy DM, Hammad MA, Aly AA. Validated spectrophotometric methods for determination of certain aminoglycosides in pharmaceutical formulations, J App Pharm Sci. 2013;3(3):151–161. https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2013.30329
Skoog DA, Holler FJ, Crouch SR. Principles of Instrumental Analysis. Thomson Brooks/Cole; 2007.
Rocha FRP, Zagatto EAG. Chemical derivatization in flow analysis. Molecules. 2022;27(5):e1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051563
Siddiqui MR, Wabaidur SM, Al Othman ZA, Ali S, Alam S. Kinetic spectrophotometric method for the quantitative analysis of streptomycin sulfate. J Chil Chem Soc. 2014;59(3). http://dx.doi.org/10.4067/S0717-97072014000300005
Vaikosen EN, Bunu SJ, Dode E, Efidi RB. Spectrophotometric fingerprinting and chemical determination of streptomycin, amikacin, neomycin, and gentamycin sulphate by condensing with ninhydrin reagent. Int J Chem Res. 2023;7(3):5–10. https://doi.org/10.22159/ijcr.2023v7i3.221
Shaikh B, Ghoto MA, Arain MA, et al. Comparative in-vitro evaluation of different captopril tablet brands commercially available in Sindh, Pakistan. J Pharm Res Intern. 2020;32(21):131–136. https://doi.org/10.9734/JPRI/2020/v32i2130763
Li Y, Su X, Peng Q, Qiao Y, Shi B. Method for determination of streptomycin and streptidine as markers for streptomycin industrial dregs monitoring in pig and poultry compound feeds. J Chromatogr B. 2016;1035:84–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.09.037
Madan LM, Geeta K, Mohammad AK, et al. Simple and fast determination of cefpodoxime and its Schiff’s base derivative using colorimeteric technique. Lat Am J Pharm. 2021;40(4):706–710.
Hiremath B, Mruthyunjayaswamy BHM. Development and validation of spectrophotometric methods for determination of ceftazidime in pharmaceutical dosage forms. Acta Pharm. 2008;58(3). https://doi.org/10.2478/v10007-008-0017-0
Shah HB, Sen AK, Aarti Z, Seth AK. Method development and validation for ceftazidime injection By Uv-Vis specrophotometer. Pharma Sci Monit. 2014;3(3):333–342.
Herrero-Hernández E, García-Gómez D, Ramírez Pérez I, Rodríguez-Gonzalo E, Pérez Pavón JL. Determination of aminoglycosides by ion-pair liquid chromatography with UV detection: application to pharmaceutical formulations and human serum samples. Molecules. 2024;29(13):e3210. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133210
Glinka M, Wasik A. Rapid determination of multiple aminoglycoside antibiotics in veterinary formulations by ion-pair chromatography coupled with evaporative light scattering detection. Microchem J. 2021;171:e106843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106843
Karande VK, Jagtap R, Kalita DJ, Ghumare BC. Determination of strepto-penicillins residues in cow milk after its intramuscular administration. J Endocrinol Zool Stud. 2021;9(2):151–156.
Savoy MC, Woo PM, Ulrich P, Tarres A, Mottier P, Desmarchelier A. Determination of 14 aminoglycosides by LC-MS/MS using molecularly imprinted polymer solid phase extraction for clean-up. Food Addit Contam Part A. 2018;35(4):675–686. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2018.1433332
Dhahir SA, Mohammed NJ. Micro spectrophotometric determination streptomycin sulfate by cloud point extraction in pure form and pharmaceutical preparation. J Pharm Sci Res. 2019;11(4):1621–1628.
Lakhoo SA, Mahesar SA, Khaskheli AR, et al. Kaolinite modified carbon paste electrode for the sensitive determination of captopril. Sen Lett. 2017;15(4):371–374. https://doi.org/10.1166/sl.2017.3830
Copyright (c) 2025 Ubed-Ur-Rehman Mughal, Madan Lal Maheshwari, Abdul Rehman Uzaid Mughal, Fozia Rustamani, Muhammad Akram Khatri, Sara Aftab, Saeed Ahmed Lakho

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 4.0 License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work’s authorship and initial publication in this journal









