Evaluation of the Antidiabetic Activity of Asphodelus Tenuifolius in Normal and Alloxan-induced Diabetic Rats
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
Asphodelus tenuifolius is traditionally used for the treatment of diabetes mellitus (DM). The current study aims to investigate the antidiabetic activity of Asphodelus tenuifolius in normal and alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Ethanolic and aqueous extracts of whole Asphodelus tenuifolius plant were prepared by using the maceration process. DM was induced by a single intraperitoneal injection of alloxan monohydrate (140 mg/kg b.w) in rats. Glibenclamide was used as the reference drug. In an acute study, ethanolic extract of Asphodelus tenuifolius (ATEE) and aqueous extract of Asphodelus tenuifolius (ATAqE) were administered in 200 and 400 mg/kg doses to normal and alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Both extracts (ATEE and ATAqE) significantly lowered the blood glucose level of both normal and diabetic treated rats in a concentration dependent fashion. However, ATEE produced prominent results at the dose of 400 mg/kg. In a fourteen-day study, ATEE considerably decreased the blood glucose level of alloxanized rats. The results were similar to the reference drug, that is, glibenclamide. In the prolonged study, the effects of ATEE on liver enzymes and hematological parameters of diabetic rats were also studied. Hb level and platelet count was increased in ATEE-treated diabetic rats as compared to diabetic control. However, it did not affect other hematological parameters. ATEE significantly decreased the ALP level as compared to diabetic control. Although, the test extract did not significantly alter the SGOT and SGPT levels. Further, the phytochemical testing of ATEE revealed the presence of alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, and terpenoids. It was concluded that Asphodeleus tenifolius possesses antidiabetic activity. More comprehensive studies are needed in the future to explicate the mechanism of action and to characterize the phyto-components of this plant.
Downloads
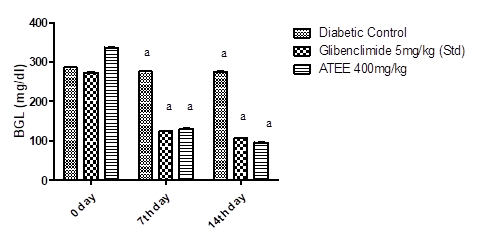
Copyright (c) 2023 Sehrish Nadeem, Irfan Iqbal Khan, Muhammad Naveed Mushtaq, Muhammad Shafeeq Ur Rahman, Shaneel Kousar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 4.0 License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work’s authorship and initial publication in this journal









