Characterization of Nicotine Degradation Associated Proteins in Paenarthrobacter nicotinovorans: An In-Silico Analysis
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
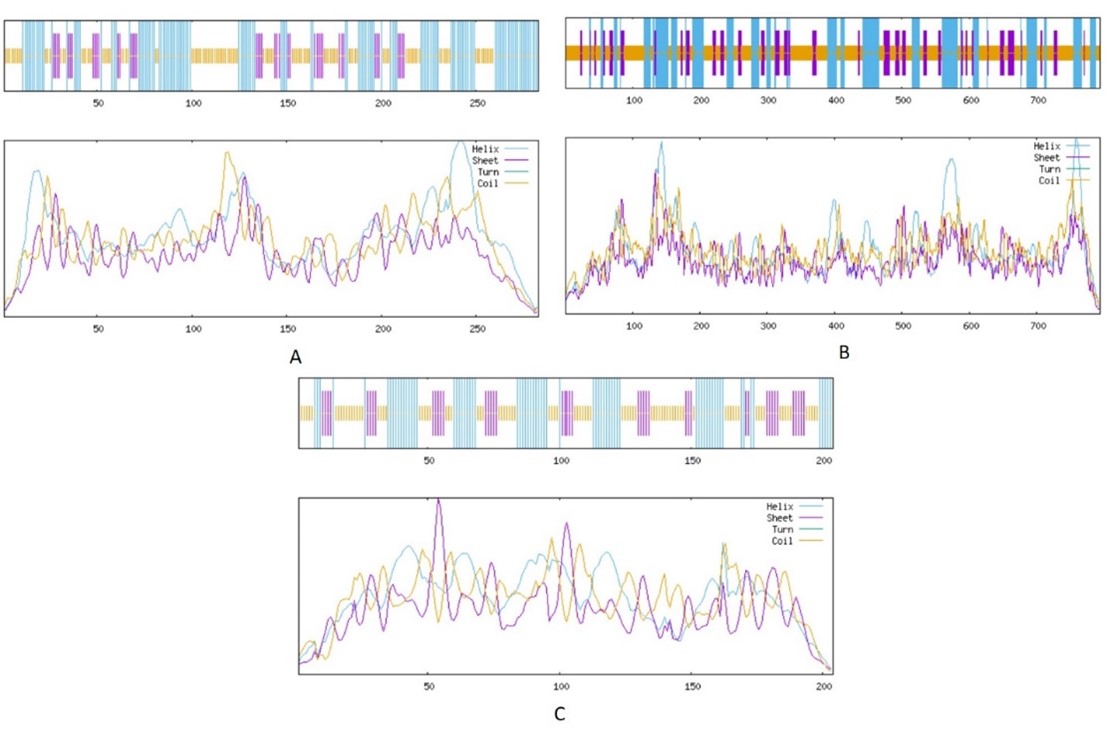
Use of nicotine degrading bacteria (NDB) to degrade nicotine from tobacco waste contaminated soil is emerging as the most promising strategy. In the current study, three nicotine degradation associated proteins from NDB Paenarthrobacter nicotinovorans i. e., nicotine dehydrogenase (ndhA), 6-hydroxypseudooxynicotine dehydrogenase (kdhL), and nicotine blue oxidoreductase (nboR) were characterized. For this purpose, coding sequences (CDS) were retrieved from Uniprot database. These sequences were then subjected to analysis via PROTPARAM tool, Multiple Em for Motif Elicitation (MEME) suite, SOPMA, SwissModel, Transmembrane Topology Prediction and Classification (TMHMM), and Peptide cutter software. Characterization revealed values of alpha helix, extended strands, and random coil ranging between (29-44%), (14.49-21.08%), and (40.99-53.65%), respectively. Instability index, aliphatic index, and grand average of hydropathy (GRAVY) were observed as 26.76-44%, 91.06-101.32%, and -0.176- 0.091%, respectively. All the proteins exhibited highly complex 3D configuration and multiple number of conserved protein motifs. The number of cleavage sites analyzed for nghA, kdhL, and nboR was 515, 1313, and 313, respectively. The characteristics explored in the current study might be used to modify these proteins in order to maximize nicotine removal from environmental sources.
Downloads
References
Pandey SK, Vishwakarma PK, Yadav SK, Shukla P, Srivastava A. Multiwalled carbon nanotube filters for toxin removal from cigarette smoke. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2019;3(1):760–771. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b02277
Wei H, Rui J, You M, et al. Materials for the selective removal of toxic compounds in cigarette smoke: a review. Sep Purif Technol. 2024:e128908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2024.12890
Ma C, Liu Y, Neumann S, Gao X. Nicotine from cigarette smoking and diet and Parkinson disease: a review. Transl Neurodegener. 2017;6:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40035-017-0090-8
Hecht SS, Hochalter JB, Villalta PW, Murphy SE. 2′-Hydroxylation of nicotine by cytochrome P450 2A6 and human liver microsomes: formation of a lung carcinogen precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97(23):12493–12497. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.220207697
Hirata N, Yamada S, Sekino Y, Kanda Y. Tobacco nitrosamine NNK increases ALDH-positive cells via ROS-Wnt signaling pathway in A549 human lung cancer cells. J Toxicol Sci. 2017;42(2):193–204. https://doi.org/10.2131/jts.42.193
Sansone L, Milani F, Fabrizi R, et al. Nicotine: from discovery to biological effects. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(19):e14570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914570
Blanc J, Tosello B, Ekblad MO, Berlin I, Netter A. Nicotine replacement therapy during pregnancy and child health outcomes: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(8):e4004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084004
McGrath-Morrow SA, Gorzkowski J, Groner JA, Rule AM, Wilson K, Tanski SE, et al. The effects of nicotine on development. Pediatrics. 2020;145(3):e20191346. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2019-1346
Gould TJ. Epigenetic and long-term effects of nicotine on biology, behavior, and health. Pharmacol Res. 2023;192:e106741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106741
Zhang Z, Mei X, He Z, et al. Nicotine metabolism pathway in bacteria: mechanism, modification, and application. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022;106(3):889–904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-11763-y
Wang Y, Luo X, Chu P, et al. Cultivation and application of nicotine-degrading bacteria and environmental functioning in tobacco planting soil. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2023;10(1):e10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-023-00630-x
Liu J, Ma G, Chen T, et al. Nicotine-degrading microorganisms and their potential applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;99:3775–3785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6525-1
Chen B, Sun L, Zeng G, et al. Gut bacteria alleviate smoking-related NASH by degrading gut nicotine. Nature. 2022;610(7932):562–568. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05299-4
Jiang Y, Gong J, Chen Y, et al. Biodegradation of nicotine and TSNAs by Bacterium sp. strain J54. Iran J Biotechnol. 2021;19(3):e2812. https://doi.org/10.30498/ijb.2021.240460.2812
Zhang K, Yin M, Lei S, Zhang H, Yin X, Niu Q. Bacillus sp. YC7 from intestines of Lasioderma serricorne degrades nicotine due to nicotine dehydrogenase. AMB Express. 2023;13(1):e87. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-023-01593-0
Xia Z-Y, Yu Q, Lei L-P, et al. A novel nicotine-degrading bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens strain 1206. Appl Biochem Microbiol. 2019;55(2):123–128.
Mu Y, Chen Q, Parales RE, et al. Bacterial catabolism of nicotine: catabolic strains, pathways and modules. Environ Res. 2020;183:e109258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109258
El-Sabeh A, Mlesnita A-M, Munteanu I-T, et al. Characterisation of the Paenarthrobacter nicotinovorans ATCC 49919 genome and identification of several strains harbouring a highly syntenic nic-genes cluster. BMC Genomics. 2023;24(1):e536.
Mihăşan M, Boiangiu RzSt, Guzun D, et al. Time-dependent analysis of Paenarthrobacter nicotinovorans pAO1 nicotine-related proteome. ACS Omega. 2021;6(22):14242–14251. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c01020
Mihăşan M, Babii C, Aslebagh R, Channaveerappa D, Dupree EJ, Darie CC. Exploration of nicotine metabolism in Paenarthrobacter nicotinovorans pAO1 by microbial proteomics. Adv Mass Spectrom Biomed Res. 2019:515–529. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15950-4_30
Mihăşan M, Babii C, Aslebagh R, Channaveerappa D, Dupree E, Darie CC. Proteomics-based analysis of the nicotine catabolism in Paenarthrobacter nicotinovorans pAO1. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):e16239. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-34687-y
Mujawar SY, Shamim K, Vaigankar DC, Naik MM, Dubey SK. Rapid arsenite oxidation by Paenarthrobacter nicotinovorans strain SSBW5: unravelling the role of GlpF, aioAB, and aioE genes. Arch Microbiol. 2023;205(10):e333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03673-y
Grether-Beck S, Igloi GL, Pust S, Schilz E, Decker K, Brandsch R. Structural analysis and molybdenum-dependent expression of the pAO1-encoded nicotine dehydrogenase genes of Arthrobacter nicotinovorans. Mol Microbiol. 1994;13(5):929–936. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00484.x
Audain E, Ramos Y, Hermjakob H, Flower DR, Perez-Riverol Y. Accurate estimation of isoelectric point of protein and peptide based on amino acid sequences. Bioinformatics. 2016;32(6):821–827. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv674
Gamage DG, Gunaratne A, Periyannan GR, Russell TG. Applicability of instability index for in vitro protein stability prediction. Protein Pept Lett. 2019;26(5):339–347. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929866526666190228144219
Morya VK, Yadav S, Kim E-K, Yadav D. In silico characterization of alkaline proteases from different species of Aspergillus. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2012;166:243–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9420-y
Copyright (c) 2025 Fatima Muccee

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Author(s) retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 4.0 License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work’s authorship and initial publication in this journal.






