Current Pharmacotherapy Trends for Hepatitis C in the Hospitals of Faisalabad, Pakistan
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 38
Abstract Views: 38
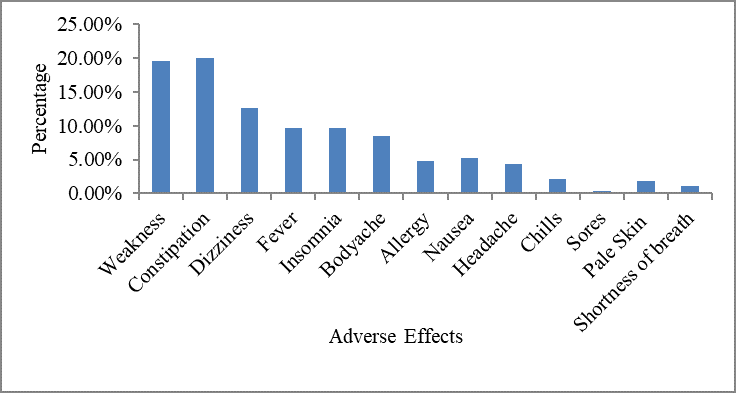
Hepatitis C infection is a global health issue. It is a growing challenge in Faisalabad, Pakistan, where at least 24% of the population is currently suffering from hepatitis C. If left untreated, HCV infection may lead to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. The current study aimed to describe the various prescription trends of hepatitis C medication therapy in Faisalabad, Pakistan. It also aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy and the satisfaction level of patients with their treatment. A comparative cross-sectional survey was carried out among patients receiving HCV medication therapy. For this purpose, a structured and close-ended questionnaire was completed by 270 patients. Comparative data analysis was performed based on selected variables, namely age, gender, marital status, current medication and its adverse effects. The prevalence of HCV in age group >40 was 63.3% and in age group <40, it was 36.7%. While, the prevalence of HCV in married individuals was 91% and its prevalence in unmarried individuals was 8.5%. Moreover, it was found that sofosbuvir was used by 24.8% of patients, daclatasvir was used by 24.4% of patients, entacavir was used by 0.4% of patients, acyclovir was used by 0.7% of patients, ribavirin was used by 7.8% of patients, and pegylated alpha 2b was used by 1.5% of patients. The trend of using combination therapy comprised interferon+ribavirin (1.5%) and velpatasvir+sofosbuvir (38.9%). The use of combination drug was found to be more common in patients of age group >40 (34.1%) than patients in age group <40 (8.8%). It was observed that lack of constant medical care and cost of therapy are major problems in the eradication of disease.
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2023 Madeeha Fatima, Aamna Habib, Faiza Habib, Kashaf Saleem, Ramsha Riaz, Sana Gulnaz, Aqsa Ahmed, Zaryab Fatima, Momina Shahid, Sadaf Waseem, Nayab Sajid, Aneeb Nadeem

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 4.0 License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work’s authorship and initial publication in this journal









