Heart-related Clinical Biomarker Classification through Machine Learning Algorithms
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
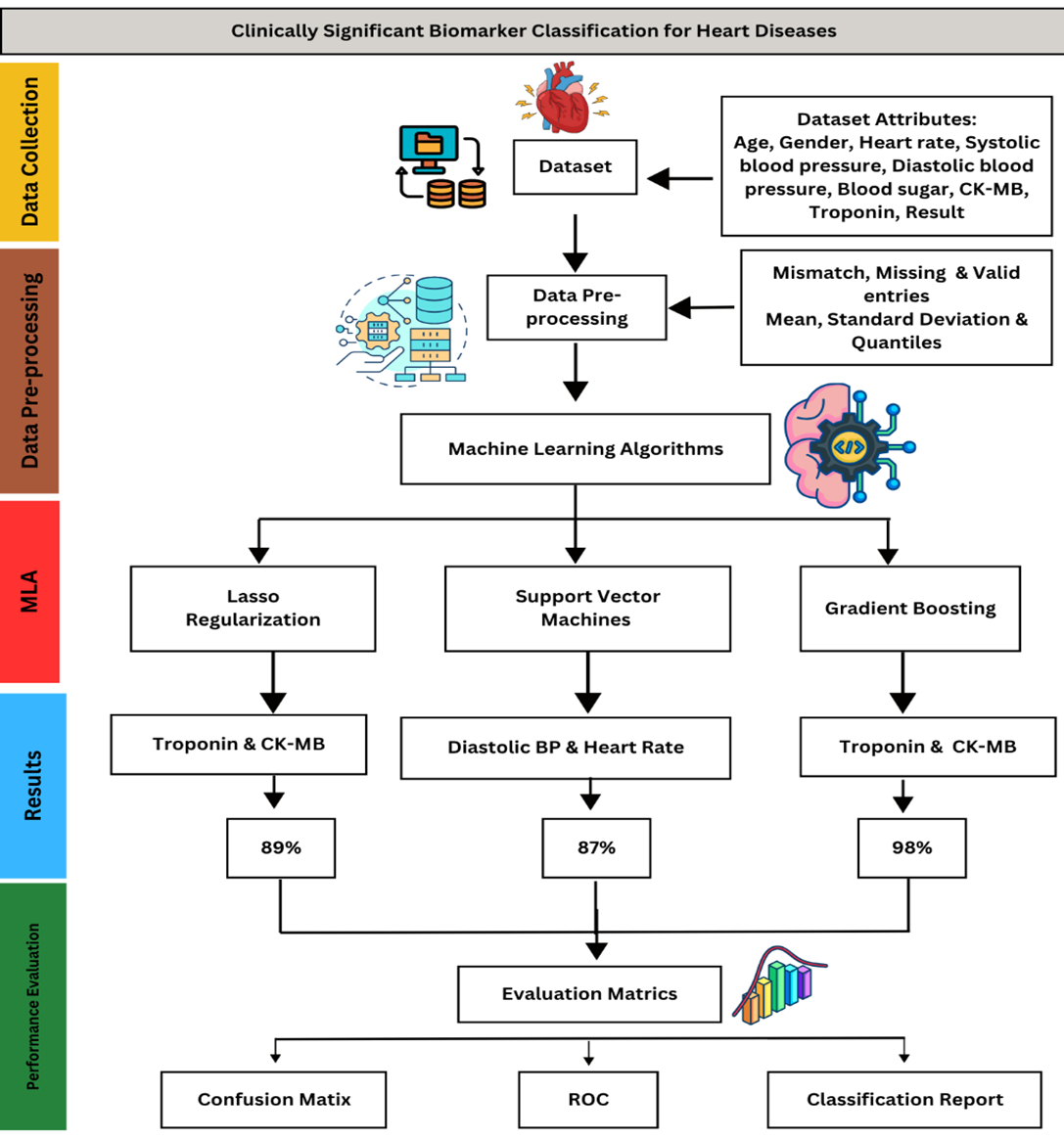
Heart diseases continue to be a major global cause of morbidity and death. Their timely and accurate diagnosis for improved patient outcomes is direly needed. Clinical biomarkers for the timely diagnosis of heart diseases are known but underutilized due to the use of conventional analytical methods that lower the efficiency to handle large datasets. Furthermore, conventional methods also fail to incorporate demographic biomarkers such as age and hemodynamic biomarkers such as heart rate and diastolic blood pressure. This significantly influences heart diseases. Using cutting edge machine learning (ML) techniques including Lasso regularization, support vector machine (SVM), and gradient boosting (GB), this study investigated the importance of clinical biomarkers for heart disease prediction. Troponin and Creatinine Kinase - MB (CK-MB) were found to be the most significant predictors among the examined characteristics in every model, underscoring their crucial importance in the diagnosis of myocardial ischemia and damage. Diastolic blood pressure was also found to be an adequate predictor, highlighting its role in increasing cardiovascular risk because of autonomous dysfunction. While SVM and GB performed strongly in managing intricate data relationships, Lasso regularization successfully decreased feature redundancy. The results support the use of clinically applicable biomarkers in conjunction with machine learning to improve the accuracy of diagnosis and also opens the door to the personalized treatment of heart disease. Validating these findings in a variety of populations and adding more biomarkers for a thorough risk assessment should be the main goals of future studies.
Downloads
References
Shah D, Patel S, Bharti SK. Heart disease prediction using machine learning techniques. SN Comput Sci. 2020;1:e345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-020-00365-y
Jevin AJ, Jayant H, Sanjay R, Hemasai V, Venkatasrinivas PV. Heart disease identification method using machine learning classification in e-healthcare. Int J Adv Res Arts Sci Eng Manag. 2023;10(3):2322–2327.
Ruetzler K, Smilowitz NR, Berger JS, et al. Diagnosis and management of patients with myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;144:e287–e305. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001024
Lakatta EG, Levy D. Arterial and cardiac aging: major shareholders in cardiovascular disease enterprises: part II: the aging heart in health: links to heart disease. Circulation. 2003;107(2):346–354. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000048893.62841.F7
Gheisari F, Emami M, Shahraki HR, Samipour S, Nematollahi P. The role of gender in the importance of risk factors for coronary artery disease. Cardiol Res Pract. 2020;2020:e527820. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6527820
Carey RM, Whelton PK. Prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: synopsis of the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association hypertension guideline. Ann Intern Med. 2018;168(5):351–358. https://doi.org/10.7326/M17-3203
Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical practice guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70(6):776–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2017.04.025
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(18):2231–2264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.08.1038
Rani P, Kumar R, Ahmed NMOS, Jain A. A decision support system for heart disease prediction based upon machine learning. J Reliab Intell Environ. 2021;7:263–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40860-021-00133-6
Saboor A, Usman M, Ali S, Samad A, Abrar MF, Ullah N. A method for improving prediction of human heart disease using machine learning algorithms. Mob Inf Syst. 2022;2022:e410169. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1410169
Ali MM, Paul BK, Ahmed K, Bui FM, Quinn JMW, Moni MA. Heart disease prediction using supervised machine learning algorithms: performance analysis and comparison. Comput Biol Med. 2021;136:e104672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104672
Feng M, Wang X, Zhao Z, Jiang C, Xiong J, Zhang N. Enhanced heart attack prediction using extreme gradient boosting. J Theo Pract Eng Sci. 2024;4(4):9–16. https://doi.org/10.53469/jtpes.2024.04(04).02
Wang Y. Identification of cardiovascular diseases based on machine learning. Paper presented at: International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence for Medicine Sciences, October 13–15, 2022; Amsterdam, Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1145/3570773.3570855
Kumar A, Dhanka S, Sharma A, et al. A hybrid framework for heart disease prediction using classical and quantum-inspired machine learning techniques. Sci Rep. 2025;15:e25040. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-09957-1
Nadakinamani RG, Reyana A, Kautish S, et al. Clinical data analysis for prediction of cardiovascular disease using machine learning techniques. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022;2023:e815067. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2973324
Rashid TA, Hassan B. Heart attack dataset. Menedleey Data Web site. Accessed April 29, 2022. http://dx.doi.org/10.17632/WMHCTCRT5V.1
Cook JA, Ranstam J. Overfitting. Br J Surg. 2016;103(13):e1814. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.10244
Wang S, Chen Y, Cui Z, Lin L, Zong Y. Diabetes risk analysis based on machine learning LASSO regression model. J Theory Pract Eng Sci. 2024;4(01):58–64. https://doi.org/10.53469/jtpes.2024.04(01).08
Cervantes J, Garcia-Lamont F, Rodríguez-Mazahua L, Lopez A. A comprehensive survey on support vector machine classification: applications, challenges and trends. Neurocomputing. 2020;408:189–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.10.118
Rauf A, Ammar M, Azhar M, Noor N, Bakhtiar SM. Unveiling the Secrets of obesity with machine learning (ml) techniques/algorithms. Curr Trend OMICS. 2024;4(1):55–76. https://doi.org/10.32350/cto.41.04
Sultan SQ, Javaid N, Alrajeh N, Aslam M. Machine learning-based stacking ensemble model for prediction of heart disease with explainable AI and K-Fold cross-validation: a symmetric approach. Symmetry. 2025;17(2):e185. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17020185
Bentéjac C, Csörgő A, Martínez-Muñoz G. A comparative analysis of gradient boosting algorithms. Artif Intell Rev. 2021;54:1937–1967. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09896-5
Primartha R, Tama BA. Anomaly detection using random forest: a performance revisited. Paper presented at: 2017 International Conference on Data and Software Engineering (ICoDSE); November 1–2, 2017; Palembang, Indonesia.
Sharma NK, Chauhan AS, Fatima S, Saxena S. Enhancing heart disease diagnosis: leveraging classification and ensemble machine learning techniques in healthcare decision-making. J Integr Sci Technol. 2024;13(1):e1016. https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.jist.2025.v13.1016
Alsabhan W, Alfadhly A. Effectiveness of machine learning models in diagnosis of heart disease: a comparative study. Sci Rep. 2025;15:e24568. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-09423-y
Khera AV, Emdin CA, Drake I, et al. Genetic risk, adherence to a healthy lifestyle, and coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(24):2349–2358. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1605086
Albahr A, Albahar M, Thanoon M, Binsawad M. Computational learning model for prediction of heart disease using machine learning based on a new regularizer. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2021;2021:e628335. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8628335
Hoque R, Billah M, Debnath A, Hossain SMS, Sharif NB. Heart disease prediction using SVM. Int J Sci Res Arch. 2024;11(2):412–420. https://doi.org/10.30574/ijsra.2024.11.2.0435
Ren W, Zhang Z, Wang Y, et al. Coronary health index based on immunoglobulin light chains to assess coronary heart disease risk with machine learning: a diagnostic trial. J Transl Med. 2025;23:e22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-024-06043-4
Uddin S, Khan A, Hossain ME, Moni MA. Comparing different supervised machine learning algorithms for disease prediction. BMC Med Informat Dec Mak 2019;19:e281. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-019-1004-8
Kwiendacz H, Huang B, Chen Y, et al. Predicting major adverse cardiac events in diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a machine learning study from the Silesia Diabetes-Heart Project. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025;24:e76. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-025-02615-w
Collet JP, Thiele H, Barbato E, et al. 2020 ESC guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(14):1289–1367. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab285
Boulet J, Sridhar VS, Bouabdallaoui N, Tardif JC, White M. Inflammation in heart failure: pathophysiology and therapeutic strategies. Inflamm Res. 2024;73:709–723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-023-01845-6
Potter JM, Hickman PE, Cullen L. Troponins in myocardial infarction and injury. Aust Prescr. 2022;45(2):53–57. https://doi.org/10.18773/austprescr.2022.006
Copyright (c) 2025 Sahar Safdar, Abdur Rauf, Shawana Qazi, Areeba Bint Tariq, Syeda Marriam Bakhtiar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Author(s) retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 4.0 License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work’s authorship and initial publication in this journal.






