Antibacterial Effects of Common Spices against Staphylococcus aureus under Laboratory Conditions
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 389
Abstract Views: 389
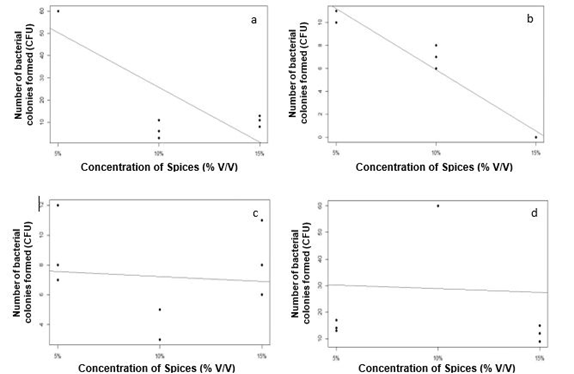
A variety of botanical extracts are currently being used for remedial purposes as they are inexpensive, safe and effective. The current study was designed to assess the antimicrobial effects of different spices such as black pepper (Piper nigrum), fennel seed (Foeniculum vulgare), carom (Trachyspermum ammi), cinnamon (Cinnamomum verum), and turmeric (Curcuma longa) against Staphylococcus aureus. The effectiveness of different spices against S. aureus was evaluated using the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) method. It was found through statistical analysis carried out using the regression method that C. verum has a significantly higher (p < 0.00) antimicrobial effect against S. aureus followed by C. longa (p = 0.005), while F. vulgare (p = 0.90) and T. ammi (p = 0.78) have a non-significant effect against S. aureus. Furthermore, P. nigrum (p = N.A) has no effect against the bacteria. The purpose of this research is to ascertain the antibacterial action of easily cultivated spices against S. aureus and the findings will be helpful in treating gastrointestinal infections using common spices instead of antibiotics.
Copyright (c) 2021 Barera Rani, Saima Naz, Saba Saeed, Ahmad Manan Mustafa Chatha
Downloads
References
Nascimento G.G.F., Locatelli J., Freitas P.C. and Silva G.L., Antibacterial activity of plant extracts and phytochemicals on antibiotic-resistant bacteria, Braz. J. Microbiol., 31, 247-256 (2000) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822000000400003
Odugbemi T., Medicinal plants as antimicrobials In: Outline and pictures of medicinal plants from Nigeria, In. University of Lagos press, 53-64 (2006)
Mostafa A.A., Al-Askar A.A., Almaary K.S., Dawoud T.M., Sholkamy E.N. and Bakri M.M., Antimicrobial activity of some plant extracts against bacterial strains causing food poisoning diseases, Saudi J. Biol. Sci., 25, 361-366 (2018) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.02.004
Zamin I., Khan I., Hyder H. and Naz B., In-vitro efficacy of crude extract of Zizipus Jujuba against selected bacterial strains, In, (2014)
Zamin I., Majid A., Ali I., Tahir A., Khan M., Ibrar J., Ali, Ullah Z., Aman I., Naveed M., Khan I., Mujaddad M. and Rahman U., In-vitro antibacterial activity of Mentha Piperita leaf extracts to some selective pathogenic bacterial strains, Int. J. Med. Pharm. Sci. Res. and Rev., 103, 1- 130 (2013)
Varahalarao V. and Chandrashekar N., In Vitro bioactivity of Indian medicinal plant Calotropis procera (Ait.), J. Glob.Pharma technol., 2, 43-45 (2010)
Alireza G., Mehdi R.R.S, Razzagh M., Ata K. and Masoud K., Antimicrobial effects of some herbal plants and spices on Staphylococcus epidermidis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Int. J.Food Nutr. Saf., 9, 40-48 (2018)
Nanasombat S., Prasertsin V., Graisin K., Shain H. and Thanaboripat D., Efficacy of new enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for rapid detection of Salmonella in foods, Government Pharmaceutical Organization Report, Bangkok, 51, 53-57 (2002)
Chaudhry N.M. and Tariq P., Bactericidal activity of black pepper, bay leaf, aniseed and coriander against oral isolates, Pak. J. Pharm. Sci., 19, 214-218 (2006)
Indu M.N., Hatha A.A.M., Abirosh C., Harsha U. and Vivekanandan G., Antimicrobial activity of some of the south-Indian spices against serotypes of Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes and Aeromonas hydrophila, Braz. J. Microbiol., 37, 153-158 (2006) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822006000200011
Aǧaoǧlu S., Dostbil N. and Alemdar S., Antimicrobial activity of some spices used in the meat industry, Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy., 51, 53-57 (2007)
Ghori I. and Ahmad S.S., Antibacterial activities of honey, sandal oil and black pepper, Pak. J. Bot., 41:461-466 (2009)
Dahanukar S., Kulkarni R. and Rege N., Pharmacology of medicinal plants and natural products. Indian J. Pharmacol., 32, 81-118 (2000)
Snyder O.P ., Antimicrobial effects of spices and herbs. In, (2013)
Pandey B., Khan S. and Singh S., A study of antimicrobial activity of some spices, Int. J. of Curr.Microbiol. Appl.Sci., 3, 643-650 (2014)
Meghwal M. and Goswami T., Nutritional constituent of black pepper as medicinal molecules: a review, Sci. Rep., 1, 129 (2012) DOI: https://doi.org/10.4172/scientificreports.129
Unlu M., Ergene E., Unlu G.V., Zeytinoglu H.S. and Vural N., Composition, antimicrobial activity and in vitro cytotoxicity of essential oil from Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume (Lauraceae), Food Chem. Toxicol., 48, 3274-3280 (2010) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.09.001
Ushimaru P.I, Silva M.T.N., Di Stasi L.C., Barbosa L. and Fernandes J.A., Antibacterial activity of medicinal plant extracts, Braz. J. Microbiol., 38, 717-719 (2007) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822007000400024
Luthra P.M, Singh R. and Chandra R., Therapeutic uses of Curcuma longa (turmeric), Indian J. Clin. Biochem., 16, 153-160 (2001) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02864854
Crellin J., Philport J. and Tommie B., A reference guide to medicinal plants: Herbal medicine past present. Duke University Press, (1989) DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctv11g96bv
Pandey B., Khan S. and Singh S., A study of antimicrobial activity of some spices, Int. J. of Curr.Microbiol. Appl.Sci., 3, 643-650 (2014)
Akhbari M., Kord R., Nodooshan S.J. and Hamedi S., Analysis and evaluation of the antimicrobial and anticancer activities of the essential oil isolated from Foeniculum vulgare from Hamedan, Iran, Nat. Prod. Res., 33, 1629-1632 (2019) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2017.1423310
Maghami M., Motalebi A.A. and Anvar S.A.A., Influence of chitosan nanoparticles and fennel essential oils (Foeniculum vulgare) on the shelf life of Huso huso fish fillets during the storage, Food Sci. Nutr.,7, 3030-3041 (2019) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.1161
Chouhan S., Sharma K. and Guleria S., Antimicrobial activity of some essential oils—present status and future perspectives. Medicines, 4, 58 (2017) DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines4030058
Soetjipto H., Antibacterial Properties of Essential Oil in Some Indonesian Herbs. Potential of Essential Oils, 41 (2018) DOI: https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.78033
Gonelimali F.D., Lin J., Miao W., Xuan J., Charles F., Chen, M. and Hatab S.R., Antimicrobial properties and mechanism of action of some plant extracts against food pathogens and spoilage microorganisms. Front Microbiol., 9,1639 (2018) DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01639
Patra A.K., An overview of antimicrobial properties of different classes of phytochemicals. Dietary Phytochemicals and Microbes, 1-32 (2012) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-3926-0_1
Cueva C., Moreno-Arribas MV., Martín-Alvarez P.J., Bills G., Vicente M.F., Basilio A., Rivas C.L., Requena T., Rodríguez J.M., Bartolomé B., Antimicrobial activity of phenolic acids against commensal, probiotic and pathogenic bacteria. Res. Microbiol., 161, 372–382 (2010) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2010.04.006
Avato P., Bucci R., Tava A., Vitali C., Rosato A., Bialy Z., Jurzysta M., Antimicrobial activity of saponins from Medicago sp.: structure-activity relationship. Phytother. Res., 20, 454–457 (2006) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.1876
Akbar A., Ali I., Samiullah N., Khan S.A., Rehman Z. and Rehman S.U., Functional, antioxidant, antimicrobial potential and food safety applications of curcuma longa and Cuminum cyminum, Pak. J. Bot., 51, 1129-1135 (2019) DOI: https://doi.org/10.30848/PJB2019-3(30)
Azarifar M., Ghanbarzadeh B., Khiabani M.S, Basti A.A., Abdulkhani A., Noshirvani N. and Hosseini M., The optimization of gelatin-CMC based active films containing chitin nanofiber and Trachyspermum ammi essential oil by response surface methodology, Carbohydr. Polym., 208, 457-468 (2019) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.01.005
Copyright (c) 2021 Barera Rani, Saima Naz, Saba Saeed, Ahmad Manan Mustafa Chatha

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
BSR follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed the Copyright and Author Consent Form.










