Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of Garlic (Allium sativum) against Common Pathogens
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 351
Abstract Views: 351
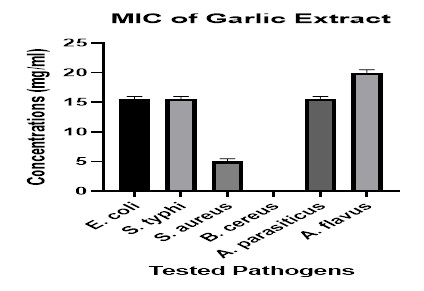
Garlic (Allium sativum) has been used worldwide to fight microbial infections. Allium sativum, in vegetable form, exhibits a high potential against pathogenic bacteria and fungi. In the current study, antimicrobial effects of pure juice, aqueous extract, ethanolic extract, and dried powder of garlic in various concentrations (100%, 75%, 50%, and 25%, respectively) against Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhi, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, Aspergillus parasiticus, and Aspergillus flavus were studied using the well diffusion technique. The results revealed that all extracts of garlic successfully inhibited the progression of E. coli, S. aureus, S. typhi, A. parasiticus, and A. flavus, while B. cereus was found to be resistant to garlic at all concentrations. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) observed against E. coli, S. typhi and A. parasiticus was 15 mg/ml, against S. aureus it was 05 mg/ml, and against A. flavus it was 20 mg/ml. Among the extracts, the antimicrobial efficacy of garlic juice was found to be better than its ethanolic extract, dried powder, and aqueous extract. It was concluded that garlic exhibits a high potential against various types of bacterial and fungal pathogens. Moreover, it also fulfills the criteria to be used as an antimicrobial agent.
Downloads
References
Strika I, Basic A, Halilovic N. Antimicrobial effects of garlic (Allium sativum L). Glas hem Tehno l Bosne Herceg. 2016;47:17-20.
Wolde T, Kuma H, Trueha K, Yabeker A. Anti-bacterial activity of garlic extract against human pathogenic bacteria. J Pharmacovigil. 2018;6(1):1-5. https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-6887.1000253
Gunda MM, Prasad RB, Odelu G, Ugandhar T. Studies on antimicrobial activity of garlic (allium sativum l.) extract against Bacillus subtilis and Aspergillus niger. Inter J Current Advan Res. 2018;1(G):9169-9171. http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/ijcar.2018.9171.1504
Nijad ASM, Shabani S, Bayat M, Hosseini SE. Antibacterial Effect of Garlic Aqueous Extract on Staphylococcus aureus in Hamburger. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2014;7(11):e13134. https://doi.org/10.5812/jjm.13134
Onyeagba RA, Ugbogu OC, Okeke CU, Iroakasi O. Studies on the antimicrobial effects of garlic (Allium sativum Linn), ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) and lime (Citrus aurantifolia Linn). African J Biotechnol. 2004;3:552-554. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB2004.000-2108
Hawassa E, Berhe A. Anti-bacterial effect of Garlic (Allium sativum) against clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli from Patients Attending Hawassa Referral Hospital, Ethiopia. J Infect Dis. 2016;2(2):15. https://doi.org/10.21767/2472-1093.100023
Lu X, Rasco BA, Jabal JMF, Aston DE, Lin M, Michael E. Investigating Antibacterial Effects of Garlic (Allium sativum) Concentrate and Garlic-Derived Organosulfur Compounds on Campylobacter jejuni by Using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, Raman Spectroscopy, and Electron Microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77(15):5257–5269. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02845-10
Tijjani A, Musa DD, Aliyu Y. Antibacterial Activity of Garlic (Allium sativum) on Staphylococcus aureus and Escherihia coli. Inter J Current Sci Stud. 2017;1(1).
Ranjan S, Dasgupta N, Saha P, Rakshit M, Ramalingam C. Comparative study of antibacterial activity of garlic and cinnamon at different temperature and its application on preservation of fish. Advan Appl Sci Res. 2012;3(1):495-501.
Wu X, Santos RR, Fink Gremmels J. Analyzing the antibacterial effects of food ingredients: model experiments with allicin and garlic extracts on biofilm formation and viability of Staphylococcus epidermi dis. Food Sci Nut. 2015;3(2):158-168. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.199
Khashan AA. Antibacterial activity of garlic extract (Allium Sativum) against Staphylococcus aureus In Vitro. Global J Bio-Sci Biotechnol. 2014;3(4):346-348.
Reiter J, Levina N, Linden M, Gruhlke M, Martin C, Slusarenko AJ. Diallylthiosulfinate (Allicin), a volatile antimicrobial from garlic (Allium sativum), kills human lung pathogenic bacteria, including MDR strains, as a vapor. Molecules. 2017;22(10):1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101711
Yadav S, Trivedi NA, Bhatt JD. Antimicrobial activity of fresh garlic juice: An in vitro study. Ayu. 2015;36(2):203-207. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-8520.175548
Gull I, Saeed M, Shaukat H, et al. Inhibitory effect of Allium sativum and Zingiber officinale extracts on clinically important drug resistant pathogenic bacteria. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2012;11(1):8-13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-0711-11-8
Khan M, Muhammad S, Abdullah, Shah SH, Israr M. In vitro antifungal potential of surfactin isolated from rhizospheric Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner 1915 against maize (Zea mays L.) fungal phytopathogen Fusarium graminearum Schwabe. Acta Agricul Sloven. 2021;117(4):1-7.
Fong J, Yuan M, Jakobsen TH, et al. Disulfide bond-containing ajoene analogues as novel quorum sensing inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Chem. 2017;60(1):215–227. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01025
Ako-NI Ak, Ikem IC, Aziba A, Ajayi AA, Onipede OA. Bacteriological examination of chronic osteomyelitis cases in lle-Ife, South Western Nigeria. Afr J Clin Exp Microbiol. 2003;4(2):41-51. https://doi.org/10.4314/ajcem.v4i2.7307
Okesola AO, Oni AA, Bakare RA. Nosocomial infections, methicillin resistant Staplylococcus aureus in wound infection in Ibadan, Nigeria. Afr J Med Med Sc. 1999;28(1):55-57.
El-Mahmood AM, Ameh JM. In vitro antibacterial activity of Parkia biglobosa (Jacq) root bark extract against some microorganisms associated with urinary infections. Afr J Biotechnol. 2007;6(11):1272-1275.
Iwalokun AB, Ogunledun DO, Ogbolu SB, Bamiro, Omojola JJ. In vitro antimicrobial properties of aqueous garlic extract against multidrug resistant bacteria and candida species from nigeria. J Med Food. 2004;7(3):327-333. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2004.7.327
Philip K, Malek SNA, Sani W, et al. Antimicrobial Activity of Some Medicinal Plants from Malaysia. Ameri J Appl Sci. 2009;6(8):1613-1617.
Sibanda T, Okoh AI. The challenges of overcoming antibiotic resistance Plant extracts: as potential sour antimicrobial and resistance modifying agents. Afr J Biotechnol. 2004;6(25):2886-2896.
https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB2007.000-2458
Acheampong YB, El-Mahmood A, Olurinola PF. Antibacterial properties of the liquid antiseptic TCP. Indian J Pharm Sci. 1988;50(3):183-186.
Copyright (c) 2022 Ziaur Rahman, Zobia Afsheen, Arshad Hussain, MUDDASIR KHAN

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
BSR follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed the Copyright and Author Consent Form.










