Insecticidal Activity of Berberis Royleana: Various Extracts against Callosobruchus Maculatus
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 99
Abstract Views: 99
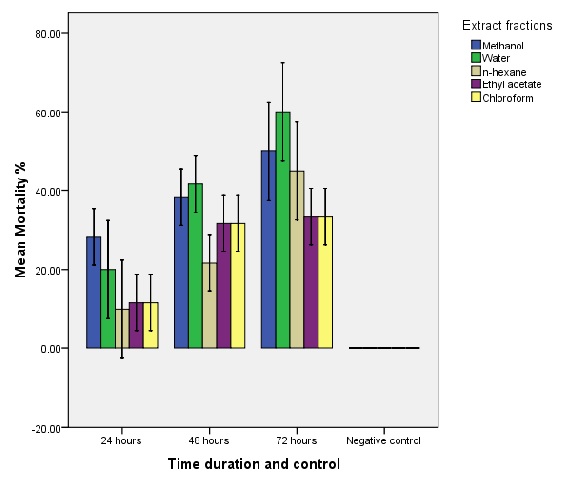
The residents of remote areas in developing countries mostly rely on traditional plants to cure different ailments. Berberis royleana is a rare species among the genus Berberis which commonly comprises 500 species distributed in Nepal, Afghanistan, Siberia, and other parts of the world. Berberis are used to make herbal medication to fight against infections, ocular trachoma, AIDS, and diarrhea. The current study was carried out to explore the in vitro insecticidal activity of B. royleana in various extracts by direct contact application process against the insect Callosobruchus maculatus. The maximum mortality rate of 60% was recorded by water fraction, whereas methanolic fraction had 50% mortality, n-Hexane had 40% mortality, while ethyl acetate and chloroform both had 30% mortality at 72 hours. Thus, this study indicated that from the medicinal point of view this specie is very significant, with a great potential for insecticidal activities against C. maculatus. It is further suggested that B. royleana could be used as a good insecticidal agent against dengue and malarial vectors. In addition, the side effects like toxicity could be addressed to avoid any mishaps.
Downloads
References
Shah Z, Ilyasa M, Khana M, Ahmada A, Khanb M, Khanc N. Antimicrobial activities of selected medicinal plants collected from Northern districts of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J Pharm Res. 2012;5(3):1729-1733.
Shinwari ZK, Qaiser MJ. Efforts on conservation and sustainable use of medicinal plants of Pakistan. Pak J Botany. 2011;43(SI):5-10.
Rehman A, Rehman A, Ahmad I. Antibacterial, antifungal, and insecticidal potentials of Oxalis corniculata and its isolated compounds. International journal of analytical Chemistry. 2015;2015:e842468. https://doi.org/doi.org/10.1155/2015/842468
Thakur DR, Devi B. Biopesticidal efficacy of Berberis lycium Linnaeus and Cannabis sativa Linnaeus against Callosobruchus chinensis Linnaeus (1758) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae). J Insect Sci. 2016;29(1):227-232.
Muhammad IC. Antibacterial, phytotoxic, insecticidal and cytotoxic potential of Vitex agnus-castus. J Med Plants Res. 2011;5(23):5642-5645.
Dad A, Ali I, Engel N, et al. The phytochemical investigation and biological activities of Berberis orthobotrys. Inter J Phytomed. 2017; 9(2):213–218. https://doi.org/10.5138/09750185.1899
Bayani M, Ahmadi-hamedani M, Jebelli Javan A. Phytochemical and antioxidant activities of berberis integerrima and berberis vulgaris and pharmacological effects of the more active species on alloxan-induced diabetic rats. J Med Plants. 2016;15(59):111-121
Mattana CM, Satorres SE, Virginia JUAN, Cifuente D, Carlos TONN, Laciar AL. Antibacterial activity study of single and combined extracts of Berberis ruscifolia, Baccharis sagittalis, Euphorbia dentata and Euphorbia schikendanzii, native plants from Argentina. B Latinoam Caribe Pl. 2012;11(5):428-434.
Furrianca MC, Alvear M, Zambrano T, Fajardo V, Salazar L. Phytochemical Constituents of the Root of Berberis Microphylla. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2017;10(6):225-227. http://dx.doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2017.v10i6.17803
Srivastava S, Srivastava M, Misra A, Pandey G, Rawat A. A review on biological and chemical diversity in Berberis (Berberidaceae). EXCLI J. 2015;14:247–267. https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2014-399
Alamgeer, Asif H, Rasool S. Antithrombotic potential of Berberis calliobotrys extract. Bangla J Pharmacol. 2016;11(4):776–783. https://doi.org/10.3329/bjp.v11i4.27054
Bibi Y, Nisa S, Chaudhary FM, Zia M. Antibacterial activity of some selected medicinal plants of Pakistan. BMC Complem Alter Med. 2011;11(1):1-7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-11-52
Siddiqui FA, Ahmad MM, Sajid MI, et al. In-Vitro Antibacterial, Antifungal, Cytotoxic and Insecticidal Activity of Various Fractions obtained from the berries of Berberis baluchistanica. Indo Euro J Sci Disco. 2016;2(2):1–6.
Ayaz F, Küçükboyaci N, Duman H, Şener B, Choudhary MI. Cytotoxic, phytotoxic and insecticidal activities of Chrysophthalmum montanum (DC.) Boiss. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2017;14(3):290-293. https://doi.org/10.4274/tjps.07279
Baloch N, Nabi S, Al-Kahraman YMSA. In vitro antimicrobial, insecticidal, antitumor activities and their phytochemical estimation of methanolic extract and its fractions of Medicago lupulina leaves. World Appl Sci J. 2013;23(4):500-506. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wasj.2013.23.04.368
Mehmood N, Zubaır M, Rızwan K, Rasool N, Shahid M, Uddin Ahmad V. Antioxidant, antimicrobial and phytochemical analysis of cichoriumintybus seeds extract and various organic fractions. Iran J Pharm Res. 2012;11(4):1145-1151.
Copyright (c) 2022 Muhammad Salman, Muhammad Rafique, MUDDASIR KHAN, Mr. Abdullah, Hayat Khan, Khalid Amin, Rooh ullah, Waqas Ashraf

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
BSR follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed the Copyright and Author Consent Form.










