Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Genes in Escherichia coli Isolated from Patients in a Tertiary Care Hospital: Implications for Clinical Management and Public Health
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
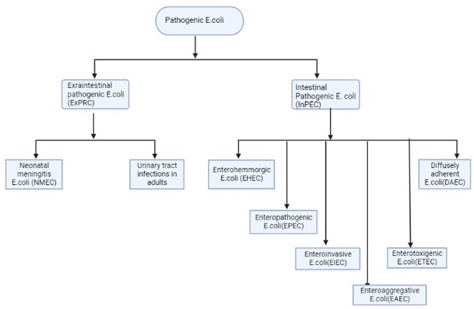
Background. Diarrheal diseases, exacerbated by limited access to clean water, remain a significant global health concern. Enterobacteriaceae, particularly Escherichia coli (E. coli), are their prevalent causative agents. The emergence of antibiotic resistance poses a grave public health threat, with extended spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBL) and carbapenemases contributing significantly. This study aimed to identify the antibiogram patterns and virulence genes in E. coli isolates obtained from patients in a tertiary care hospital.
Method. A cross-sectional study involving 395 clinical samples from tertiary care hospital of Lahore was conducted over a period of six months. The isolation and characterization of bacterial strains were performed using culture-based, biochemical, and morphological assessments. Antibiotic susceptibility testing (AST) was carried out using the Kirby-Bauer (KB) disk diffusion method. DNA extraction and molecular identification of virulence genes were conducted through PCR. Statistical analysis was performed using Excel and SPSS.
Results. Of the 395 samples, E. coli was found to be the most prevalent (47.6%), followed by Klebsiella spp. (43.3%). AST revealed high resistance to cefuroxime (85%) and ciprofloxacin (80%). Molecular analysis identified virulence genes with traT being the most prevalent (37.2%), followed by fimH and aer (28.7%). Notably, sfa, papA, hly, and cnf genes were undetected.
Conclusion. The results showed the prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes and virulence factors in E. coli isolates in patients from a tertiary care hospital. The high resistance rates necessitate vigilant antimicrobial stewardship. The presence of specific virulence genes emphasizes the potential pathogenicity of these isolates, underscoring the importance of effective infection control measures.
Downloads
References
Adrees U, Afzal I, Chaudhary AS, Zia R, Ali K. Sources and prevalence of aflatoxin B1 in different rice paddies of Punjab and Sindh, Pakistan. BioSci Rev. 2023;5(2):18–25. https://doi.org/10.32350/BSR.52.03
Ahmad I, Masuda G, Tomohiko S, Shabbir CA. Living well as a Muslim through the pandemic era—a qualitative study in Japan. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(10):e6020. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/ijerph19106020
Akunda IK, Kariuki DW, Matulis G, et al. Antimicrobial resistance patterns and characterisation of emerging beta‐lactamase‐producing Escherichia coli in camels sampled from Northern Kenya. Vet Med Sci. 2023;9(3):1407–1416. https://doi.org/10.1002/vms3. 1090
Asadi S, Kargar M, Solhjoo K, et al. The association of virulence determinants of uropathogenic Escherichia coli with antibiotic resistance. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2014;7(5):e9936. https://doi.org/10. 5812%2Fjjm.9936
Ejaz H, Imran M, Zafar A, et al. Phenotypic characterisation of carbapenemase-producing Escherichia coli isolated from a tertiary care paediatric hospital. Int Med J. 2020;27(2):155–158.
Farooqi MA, Ahsan A, Yousuf S, Shakoor N, Farooqi HMU. Seroprevalence of hepatitis E virus antibodies (IgG) in the community of Rawalpindi. Livers. 2022;2(3):108–115. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers2030009
Fatima S, Akbar A, Irfan M, et al. Virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance of uropathogenic Escherichia coli EQ101 UPEC isolated from UTI patient in Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan. Biomed Res Int. 2023;2023:e7278070. https://doi.org /10.1155/2023/7278070
Firoozeh F, Saffari M, Neamati F, Zibaei M. Detection of virulence genes in Escherichia coli isolated from patients with cystitis and pyelonephritis. Int J Infect Dis. 2014;29:219–222. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.ijid.2014.03.1393
Fonseca-Martínez SA, Martínez-Vega RA, Farfán-García AE, González Rugeles CI, Criado-Guerrero LY. Association between uropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence genes and severity of infection and resistance to antibiotics. Infect Drug Resist. 2023;16:3707–3718.
Foxman B, Manning SD, Tallman P, et al. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli are more likely than commensal E. coli to be shared between heterosexual sex partners. Am J Epidemiol. 2002;156(12):1133–1140. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwf159
Ibrahim DR, Dodd CE, Stekel DJ, et al. Multidrug-resistant ESBL-producing E. coli in clinical samples from the UK. Antibiotics. 2023;12(1):e169. https:// doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12010169
Jalali HR, Pourbakhsh A, Fallah F, Eslami G. Genotyping of virulence factors of uropathogenic Escherichia coli by PCR. Novelty Biomed. 2015;3(4):177–181. https://doi.org/ 10.22037/nbm.v3i4.8036
Karimian A, Momtaz H, Madani M. Detection of uropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence factors in patients with urinary tract infections in Iran. Afr J Microbiol Res. 2012;6(39):6811–6816.
Kathayat D, Lokesh D, Ranjit S, Rajashekara G. Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC): An overview of virulence and pathogenesis factors, zoonotic potential, and control strategies. Pathogens. 2021;10(4):e467. https://doi.org/10. 3390/pathogens10040467
Kawalec A, Józefiak J, Kiliś-Pstrusińska K. Urinary tract infection and antimicrobial resistance patterns: 5-year experience in a tertiary pediatric nephrology center in the Southwestern region of Poland. Antibiotics. 2023;12(9):e1454. https://doi.org /10.3390/antibiotics12091454
Lee JH, Subhadra B, Son YJ, et al. Phylogenetic group distributions, virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance properties of uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from patients with urinary tract infections in South Korea. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2016;62(1):84–90. https://doi.org/ 10.1111/lam.12517
Momtaz H, Karimian A, Madani M, et al. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli in Iran: serogroup distributions, virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance properties. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2013;12:1–12. https://doi. org/10.1186/1476-0711-12-8
Morales-López S, Yepes JA, Prada-Herrera JC, Torres-Jiménez A. Enterobacteria in the 21st century: a review focused on taxonomic changes. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2019;13(04):265–273. https://doi.org/10.3855/jidc.11216
Neamati F, Firoozeh F, Saffari M, Zibaei M. Virulence genes and antimicrobial resistance pattern in uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from hospitalized patients in Kashan, Iran. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2015;8(2):e17514. https://doi.org/ 10.5812%2Fjjm.17514
Odonkor ST, Simpson SV, Medina MWR, Fahrenfeld N. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria and resistance genes in isolates from Ghanaian drinking water sources. J Environ Public Health. 2022;2022(1):e2850165.
Raeispour M, Ranjbar R. Antibiotic resistance, virulence factors and genotyping of uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2018;7(1):1–9.
Riaz M, Ejaz H, Zafar A, et al. Current trends in multidrug-resistant AmpC beta-lactamase producing Enterobacter cloacae isolated from a tertiary care hospital. Bangladesh J Med Sci. 2020;19(4):632–637. https://doi.org/10.3329/bjms.v19i4.46618.
Shoaib N, Noureen N, Faisal A, et al. Factors associated with cycle threshold values (Ct-values) of SARS-CoV2-rRT-PCR. Mol Biol Rep. 2022;49(5):4101–4106. https://doi. org/10.1007/s11033-022-07360-x
Spurbeck RR, Dinh PC, Jr., Walk ST, et al. Escherichia coli isolates that carry vat, fyuA, chuA, and yfcV efficiently colonize the urinary tract. Infect Immun. 2012;80(12):4115–4122. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.00752-12
Tarchouna M, Ferjani A, Ben-Selma W, Boukadida J. Distribution of uropathogenic virulence genes in Escherichia coli isolated from patients with urinary tract infection. Int J Infect Dis. 2013;17(6):e450–e453. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.ijid.2013.01.025
Wang Q, Zhao K, Guo C, et al. Antibiotic resistance and virulence genes of Escherichia coli isolated from patients with urinary tract infections after kidney transplantation from deceased donors. Infect Drug Resist. 2021:4039–4046.
Yun KW, Kim HY, Park HK, Kim W, Lim IS. Virulence factors of uropathogenic Escherichia coli of urinary tract infections and asymptomatic bacteriuria in children. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2014;47(6):455–461. https://doi.org /10.1016/j.jmii.2013.07.010
Zahid AS, Farooqi HMU, Ahsan A, et al. Comparative analysis of antigenic strength and in vivo serum antibodies concentration of tetanus toxoid vaccine adsorbed in Pakistan. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022;29(8):e103337. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103337
Ahmad I, Taimur H, Shabbir S, et al. Examining communicative, critical health literacy and ehealth literacy among international university students residing in Japan. Healthcare. 2024;12(9):e941. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/healthcare12090941
Ahsan A, Shabbir CA, Qadeer MA, et al. Comparison of rapid antigen test with RT-PCR for COVID-19 diagnosis: performance and limitation. Russ Open Med J. 2024;13(2):e0210. https://doi.org/10.15275/rusomj.2024.0210
Khan R, Javed H, Fatima W, et al. The unspoken wounds: understanding the psychological impact on healthcare professionals fighting COVID‐19 in Pakistan. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2024;2024(1):e3364960. https://doi. org/10.1155/2024/3364960
Ahsan A, Gull S, Imran H, Khan Z. Mechanistic insights of colistin resistance and its public health implications. Appl Biochem Microbiol. 2023;59(5):597–607. https://doi.org /10.1134/S0003683823050022
Zorob T, Farooqi MA, Ahsan A, Zaki A, Rathore MA, Farooqi HM. Prevalence and trends in hepatitis B & C virus among blood donors in Pakistan: a regional transfusion center study. Livers. 2023;3(2):271–281. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers3020018
Ali A, Shahbaz M, Wali M, et al. Antibiogram assay of E. coli isolated from pus samples at Lady Reading Hospital Peshawar. Nat Volat Essent Oils J. 2021;8(5):7411–7415.
Copyright (c) 2024 Ali Ahsan, Fatima Tul Zahra, Alina Asif , Muhammad Fawad , Tazeela Mariam , Maliha Mazhar , Muhammad Abdul Qadeer, Adnan Yaseen , Muhammad Ilyas, Muhammad Annes Sharif

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
BSR follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed the Copyright and Author Consent Form.










