Seroepidemiology of Human Cytomegalovirus and Human Herpesvirus 6 in a Cohort of Healthy Blood Donors from Abbottabad, Pakistan
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
Background. Human Cytomegalovirus (CMV) and Human Herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) represent significant public health concerns due to their widespread prevalence and potential clinical sequelae. This study aimed to elucidate the sero-epidemiological profile of CMV and HHV-6 among a cohort of ostensibly healthy blood donors in Abbottabad, Pakistan.
Methods. A cross-sectional study was conducted from December 2021 to June 2022 at the Regional Blood Centre in Abbottabad. Initially, 1850 healthy male blood donors were recruited according to WHO criteria, with 1750 meeting eligibility after screening for high-risk behaviors and clinical symptoms. Plasma samples were assayed for anti-CMV IgG, CMV IgM, and HHV-6 IgM using ELISA kits (sensitivity: 99%, specificity: 95%), with optical density measured at 450/620 nm. Donors were stratified into four age groups (<18, 21–30, 31–40, and 41–50 years) and statistical analyses were performed using descriptive statistics and Pearson’s Chi-square test (p<0.05) in SPSS (version 25). Of the 1850 initially recruited donors, 1750 met the inclusion criteria (mean age: 28.2 years; range: 19–50 years).
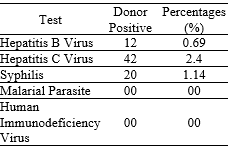
Results. Initial screening revealed low prevalence rates for HBsAg (0.69%), anti-HCV (2.4%), and syphilis (1.14%), with all donors testing negative for malarial parasites and HIV. Blood group distribution was predominantly O (36%) and B (36%), with 96% of donors being Rh-positive. Overall, serological assessment demonstrated a CMV IgG seroprevalence of 90.2%, CMV IgM positivity in 5.7%, and HHV-6 IgM positivity in 8% of donors. Age-stratified analysis indicated: donors aged <18 years exhibited 80% CMV IgG positivity (with no CMV IgM or HHV-6 IgM), those aged 21–30 years 89% CMV IgG, 5.45% CMV IgM, and 9.1% HHV-6 IgM positivity; donors aged 31–40 years showed 94.2% CMV IgG, 7.69% CMV IgM, and 7.6% HHV-6 IgM positivity; while donors aged 41–50 years demonstrated universal CMV IgG positivity without detectable CMV IgM or HHV-6 IgM.
Conclusion. The elevated CMV IgG seroprevalence among Abbottabad blood donors indicates widespread viral exposure, while the lower rates of CMV IgM and HHV-6 IgM suggest infrequent recent or reactivated infections. These findings underscore the need for continued sero-epidemiological surveillance to inform and optimize regional blood safety protocols.
Downloads
References
Cheema S, Rana V, Kulhari K, Yadav A, Sachdeva A. Prevalence of transfusion transmissible infections and associated factors among healthy blood donors in North Indian population–4-Year experience of licensed blood bank at tertiary care hospital. J Marine Med Soc. 2022;24(3):S47–S52. https://doi.org/ 10.4103/jmms.jmms_167_20
Saba N, Nasir JA, Waheed U, et al. Seroprevalence of transfusion-transmitted infections among voluntary and replacement blood donors at the Peshawar Regional Blood Centre, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J Lab Phy. 2021;13(02):162–168. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1729485
King O, Al Khalili Y. Herpes Virus Type 6. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
Al-Sadeq DW, Zedan HT, Aldewik N, et al. Human herpes simplex virus-6 (HHV-6) detection and seroprevalence among Qatari nationals and immigrants residing in Qatar. IJID Regions. 2022;2:90–95. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.ijregi.2021.12.005
Luscalov S, Loga L, Dican L, Junie LM. Cytomegalovirus infection in immunosuppressed patients after kidney transplantation. Clujul Med. 2016;89(3):343–346. https://doi.org/10.15386/cjmed-587
Gabrielli L, Balboni A, Borgatti EC, et al. Inherited chromosomally integrated human herpesvirus 6: laboratory and clinical features. Microorganisms. 2023;11(3):eE548. https://doi.org/10. 3390/microorganisms11030548
Adane T, Getawa S. Cytomegalovirus seroprevalence among blood donors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Int Med Res. 2021;49(8):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1177/03000605211034656
Xia W, Yan H, Zhang Y, et al. Congenital human cytomegalovirus infection inducing sensorineural hearing loss. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:e824. https://doi.org/10. 3389/fmicb.2021.649690
Zuhair M, Smit GSA, Wallis G, et al. Estimation of the worldwide seroprevalence of cytomegalovirus: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Rev Med Virol. 2019;29(3):e2034. https://doi.org/10.1002/rmv.2034
Traore L, Tao I, Bisseye C, et al. Molecular diagnostic of cytomegalovirus, Epstein Barr virus and Herpes virus 6 infections among blood donors by multiplex real-time PCR in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. Pan Afr Med J. 2016;24:e298. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2016.24.298.6578
Politou M, Koutras D, Kaparos G, et al. Seroprevalence of HHV-6 and HHV-8 among blood donors in Greece. Virol J. 2014;11(1):e153. https://doi.org/ 10.1186/1743-422X-11-153
Schattner A. The Wide Spectrum of Presentations of Cytomegalovirus Infection in Immunocompetent Hosts: An Exhaustive Narrative Review. Pathogens. 2024; 13(8):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13080667
World Health Organization. Blood donor selection: guidelines on assessing donor suitability for blood donation. WHO Web site. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241548519. Updated January 1, 2012.
Mahallawi W, Khabour OF, Al-Saedi A, Almuzaini Z, Ibrahim N. Human cytomegalovirus seroprevalence among blood donors in the Madinah Region, Saudi Arabia. Cureus. 2022;14(2):e21860. https://doi.org/ 10.7759/cureus.21860
Ibrahim S, Siddiqui AA, Siddiqui AR, Ahmed W, Moss PA, Lalani E-N. Sociodemographic factors associated with IgG and IgM seroprevalence for human cytomegalovirus infection in adult populations of Pakistan: a seroprevalence survey. BMC Public Health. 2016;16(1):e1112. https://doi. org/10.1186/s12889-016-3772-8
Staras SA, Dollard SC, Radford KW, Flanders WD, Pass RF, Cannon MJ. Seroprevalence of cytomegalovirus infection in the United States, 1988–1994. Clinic Infect Dis. 2006;43(9):1143–1151. https://doi.org/10.1086/508173
Blankson PK, Parkins GE, Blankson HN, Fasola AO, Pappoe-Ashong PJ, Boamah MO, Asmah RH. Herpesviruses and human papillomaviruses in saliva and biopsies of patients with orofacial tumors. Clinics.2024;14;79:100477. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.clinsp.2024.100477
Lübeck PR, Doerr HW, Rabenau HF. Epidemiology of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) in an urban region of Germany: what has changed? Med Microbiol Immunol. 2010;199:53–60. https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s00430-009-0136-3
Lopo S, Vinagre E, Palminha P, Paixão MT, Nogueira P, Freitas MG. Seroprevalence to cytomegalovirus in the Portuguese population, 2002-2003. Eurosurveillance.2011;16(25):e19896.
Olusanya BO, Slusher TM, Boppana SB. Prevalence of congenital cytomegalovirus infection in Nigeria: a pilot study. Pediat Infect Dis J. 2015;34(3):322–324.
Britt WJ. Maternal immunity and the natural history of congenital human cytomegalovirus infection. Viruses. 2018;10(8):e405. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/v10080405
Cannon MJ, Schmid DS, Hyde TB. Review of cytomegalovirus seroprevalence and demographic characteristics associated with infection. Rev Med Virol. 2010;20(4):202–213. https://doi. org/10.1002/rmv.655
Fowler K, Mucha J, Neumann M, et al. A systematic literature review of the global seroprevalence of cytomegalovirus: possible implications for treatment, screening, and vaccine development. BMC Public Health. 2022;22(1):e1659. https://doi. org/10.1186/s12889-022-13971-7
Rizvi CB, Raza A, Siddiqui MF. Sero-prevalence of human cytomegalovirus among blood donors in Lahore, Pakistan. Advanc Life Sci. 2015;2(4):171–175. http://dx.doi.org/ 10.62940/als.v2i4.132
Umeh E, Onoja T, Aguoru C, Umeh J. Seroprevalence of cytomegalovirus antibodies in pregnant women, Benue State, Nigeria. J Infect Dis Ther. 2015;3(242):e2332-0877.
Souza MA, Passos AM, Treitinger A, Spada C. Seroprevalence of cytomegalovirus antibodies in blood donors in southern, Brazil. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2010;43:359–361. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0037-86822010000400004
Mustakangas P, Sarna S, Ämmälä P, Muttilainen M, Koskela P, Koskiniemi M. Human cytomegalovirus seroprevalence in three socioeconomically different urban areas during the first trimester: a population-based cohort study. Int J Epidemiol. 2000;29(3):587–591. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/29.3.587
Ahmed HA, Fares KK, Al-Barzinji RM. Cytomegalovirus seropositivity among voluntary blood donors in Koya. J Rasp Univ. 2016;3(6):73–78.
Henry N, Baiju NM, Bhaskaran R, Sudha S, Thomas T. Cytomegalovirus seroprevalence among blood donors in Kerala. Int J Contemp Med Res. 2016;3(10):e77.83.
Britt W. Manifestations of human cytomegalovirus infection: proposed mechanisms of acute and chronic disease. In: Shenk TE, Stinski MF, eds. Human Cytomegalovirus. Springer Nature; 2008:417–470.
Nogalski M, Collins-McMillen D, Yurochko A. Overview of human cytomegalovirus pathogenesis. In: Yurochko AD, Miller WE, eds. Human Cytomegaloviruses. Springer; 15–28:2014.
Sultanova A, Cistjakovs M, Sokolovska L, Cunskis E, Murovska M. Investigation of the involvement of HHV-6 encoded viral chemokine receptors in autoimmune thyroiditis development. Microbiol Spect. 2022;10(3):e02369-21. https://doi.org/ 10.1128/spectrum.02369-21
Keshavarz M, Ghasemi S, Arjeini Y, et al. Frequency evaluation and molecular characterization of HHV‐6 and HHV‐7 among children under 5 years with fever and skin rash. J Med Virol.2023;95(3):e28608. https://doi. org/10.1002/jmv.28608
Copyright (c) 2025 Nayyab Iftikhar, Aamer Ali Khattak, Usman Ayub Awan, Anas Saeed, Hassan Ayaz, Hajra Iqbal Khan, Mishal Bibi, Farakh Javed, Umair Farukh, Muhammad Subhan Fareed

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
BSR follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed the Copyright and Author Consent Form.










