Influence of Energy Drinks on Different Cardiovascular Parameters of Healthy Young Adults: A Pilot Study
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
Background. Energy drink (ED) intake is associated with acute changes in cardiovascular indices. However, the amplitude of electrocardiographic (ECG) waves have been scarcely studied and gender difference has not been explored either. The current study aims to observe changes in ECG under the influence of ED with focusing on gender differences.
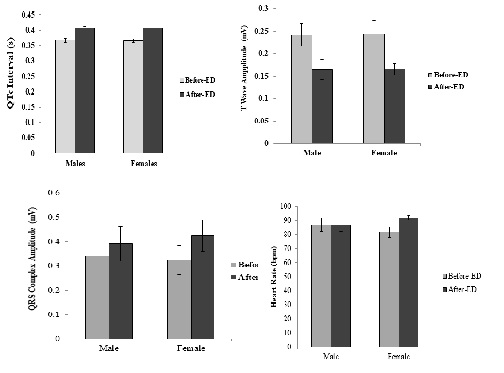
Methods. Twenty healthy participants with an average age of 22 years were enrolled in this study. Half of the participants were male and half were female. This study was conducted in the Department of Physiology, University of Karachi from July 2019 to October 2019. The participants were asked to drink 500 ml of ED. Later limb lead ECG was performed before (Before-ED) and 2 hours after (After-ED) intake. Recording and data analysis was done through Powerlab. Heart rate (HR) corrected QT interval (QTc), R wave, and T wave amplitudes and HR were calculated and analyzed.
Results. QTc was found to increase (10%) in After-ED as compared to Before-ED. In contrast, T wave was found to reduce (37%) in After-ED. These results were statistically significant (p < 0.05). These changes in QTc and T waves were similar in both male and female subjects. The HR did not change in males. In females, it increased from an average of 82 bpm in Before-ED to 92 bpm in After-ED and the difference was statistically significant (p < 0.05).
Conclusion. Acute intake of energy drinks produces acute changes in ECG with no gender difference. Thus, regular intake of these drinks should be avoided.
Downloads
References
Farber J, Dikdan S, Ruge M, Johnson D, Shipon D. Relationship between Caffeine consumption and young athletes’ comorbidities, exercise-related symptoms, and baseline electrocardiogram. Sports Health. 2023;10(3):448–456. https://doi.org/10.1177/19417381231168828
Shah SA, Occiano A, Nguyen TA, et al. Electrocardiographic and blood pressure effects of energy drinks and Panax ginseng in healthy volunteers: a randomized clinical trial. Int J Cardiol. 2016;218:318–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.05.007
Fletcher EA, Lacey CS, Aaron M, Kolasa M, Occiano A, Shah SA. Randomized controlled trial of high‐volume energy drink versus Caffeine consumption on ECG and hemodynamic parameters. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6(5):e004448. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.116.004448
Copyright (c) 2025 Fayzan Akhtar, Arifa Savanur, Quratulain Zia, Mudassir Rizvi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
BSR follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed the Copyright and Author Consent Form.










