Prevalence of HCV-Helicobacter pylori co-infection and its effects on liver function enzymes of patients in Lahore, Pakistan
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 220
Abstract Views: 220
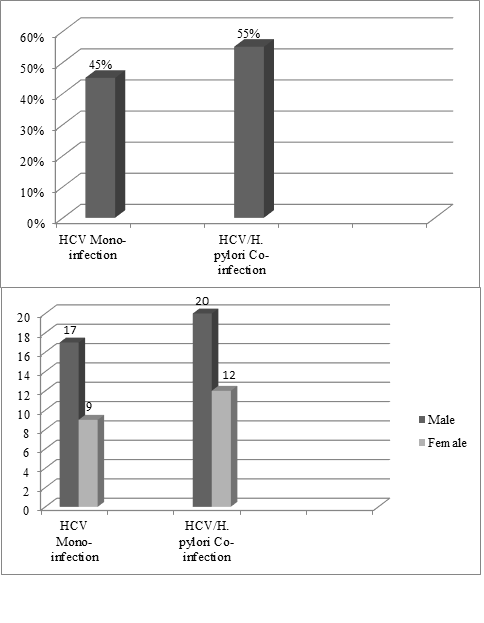
Helicobacter pylori and HCV are the most prevalent pathogens worldwide associated with high rates of morbidity and mortality. This study aimed to determine the prevalence of H. pylori in HCV infected patients and compares changes in liver function tests (LFTs) of both HCV mono-infected and HCV/H. pylori co-infected patients. Eighty-seven participants participated in this study who were first screened for HCV using GeneXpert technology followed by H. pylori antigen stool test. A complete blood count (CBC) analysis and LFTs were performed to determine the impact of HCV and H. pylori on liver enzymes. Our findings suggested that 45% of patients had HCV mono-infection, whereas 55% were co-infected with both HCV and H. pylori. Furthermore, we also observed that ALT, AST, and ALP levels were significantly elevated in HCV/H. pylori co-infected patients as compared to HCV mono-infected patients. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to report the prevalence of H. pylori in HCV infected subjects of Lahori population
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2019 Sohaib Bin Wahid, Muhammad Waqar, Zobaria Rehman, Muhammad Wasim, Muhammad Idrees

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
BSR follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed the Copyright and Author Consent Form.










