Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk: Lipid Profile Changes Due to Pesti-cide Exposure in Agricultural Sprayers - A Case-Control Study
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
Introduction. There are several threats to the human body from the potentially hazardous chemicals used in crop fields, such as pesticides. This investigation aims to assess variations in the serum lipid profile associated with pesticide exposure.
Methodology. For this case-control study, 131 participants were recruited. These included 71 pesticide sprayers and 60 healthy individuals who served as the control group, all from the rural areas of South Punjab, Pakistan. The lipid biomarkers of the participants were evaluated using a biochemistry analyzer and the results were statistically analyzed through GraphPad Prism.
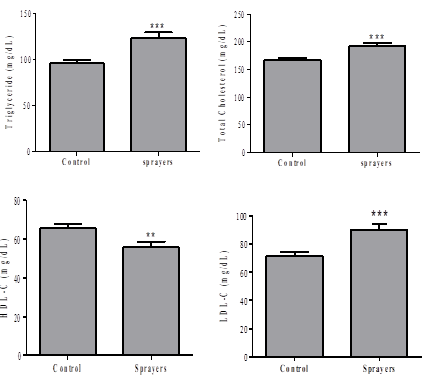
Results. The results indicated that TG (triglycerides) and TC (total cholesterol) levels significantly (p<0.001) increased with a prominent increase in LDL-C (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol) and VLDL-C (very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol) (p<0.001 and 0.011 respectively). However, a significant decrease in HDL-C (high-density lipoprotein cholesterol) (p=0.006) was observed in sprayers as compared to the control group.
Conclusion. These alterations may be attributed to oxidative stress and hepatic dysfunction induced by prolonged pesticide exposure. The results are based on the hypothesis that significant alterations in the lipid profile anticipate potential health risks associated with pesticide exposure.
Introduction. There are several threats to the human body from the potentially hazardous chemicals used in crop fields, such as pesticides. This investigation aims to assess variations in the serum lipid profile associated with pesticide exposure.
Methodology. For this case-control study, 131 participants were recruited. These included 71 pesticide sprayers and 60 healthy individuals who served as the control group, all from the rural areas of South Punjab, Pakistan. The lipid biomarkers of the participants were evaluated using a biochemistry analyzer and the results were statistically analyzed through GraphPad Prism.
Results. The results indicated that TG (triglycerides) and TC (total cholesterol) levels significantly (p<0.001) increased with a prominent increase in LDL-C (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol) and VLDL-C (very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol) (p<0.001 and 0.011 respectively). However, a significant decrease in HDL-C (high-density lipoprotein cholesterol) (p=0.006) was observed in sprayers as compared to the control group.
Conclusion. These alterations may be attributed to oxidative stress and hepatic dysfunction induced by prolonged pesticide exposure. The results are based on the hypothesis that significant alterations in the lipid profile anticipate potential health risks associated with pesticide exposure.
Downloads
References
Kalyabina VP, Esimbekova EN, Kopylova KV, Kratasyuk VA. Pesticides: formulants, distribution pathways and effects on human health–a review. Toxicol Rep. 2021;8:1179–1192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.06.004
Yassi A, Kjellström T, De Kok T, Guidotti TL. Basic Environmental Health. Oxford University Press; 2001.
Ali S, Ullah MI, Sajjad A, Shakeel Q, Hussain A. Environmental and health effects of pesticide residues. In: Inamuddin, Ahamed MI, Lichtfouse E, eds. Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 48: Pesticide Occurrence, Analysis and Remediation Vol 2 Analysis. Springer Nature; 2021:311–336.
Azmi MA, Naqvi S, Azmi MA, Aslam M. Effect of pesticide residues on health and different enzyme levels in the blood of farm workers from Gadap (rural area) Karachi—Pakistan. Chemosphere. 2006;64(10):1739–1744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.01.016
The study examined farm workers from 14 different fruit and vegetable farm stations in Gadap, Karachi-Pakistan for the presence of pesticide residues in their blood samples. The study found a significant increase in enzyme levels (GPT, GOT, and ALP) in the exposed individuals, who also reported liver and kidney dysfunctions, as well as respiratory tract infections (RTI).
Anjum AS, Zada R, Tareen WH. Organic farming: hope for the sustainable livelihoods of future generations in Pakistan. J Pure Appl Agricul. 2016;1(1):20–29.
Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations. Pesticides use. July 2024 update. https://www.fao.org/statistics/events/events-detail/pesticides-use.-july-2024-update/en. Updated July 7, 2024. Accessed January 17, 2025.
Van Maele-Fabry G, Lantin A-C, Hoet P, Lison D. Childhood leukaemia and parental occupational exposure to pesticides: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Cont. 2010;21(6):787–809. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-010-9516-7
Sharon M, Bhawana M, Anita S. A short review on how pesticides affect human health. Int J Ayurved Herbal Med. 2012;2(5):935–946.
de Moraes Mello Boccolini P, Boccolini CS, de Rezende Chrisman J, Koifman RJ, Meyer A. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma among Brazilian agricultural workers: A death certificate case-control study. Arch Environ Occup Health. 2017;72(3):139–144. https://doi.org/10.1080/19338244.2016.1179167
This study examined Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) mortality risk in agricultural workers in southern Brazil. A higher risk was found among those aged 20-39 but not associated with ethnicity or state of residence. Low education levels in agricultural workers were suggested as a possible factor linked to increased NHL mortality, potentially due to unsafe pesticide handling.
Gunier RB, Kang A, Hammond SK, et al. A task-based assessment of parental occupational exposure to pesticides and childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Environ Res. 2017;156:57–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.03.001
Zago AM, Faria NMX, Fávero JL, Meucci RD, Woskie S, Fassa AG. Pesticide exposure and risk of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review. Global Public Health. 2022;17(12):3944–3966. https://doi.org/10.1080/17441692.2020.1808693
Yokus B, Cakir D, Kanay Z, Gulten T, Uysal E. Effects of seasonal and physiological variations on the serum chemistry, vitamins and thyroid hormone concentrations in sheep. J Veter Med Ser A. 2006;53(6):271–276. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0442.2006.00831.x
The study on Sakiz-Awassi crossbreed sheep explored serum chemistry, noting variations in total protein, cholesterol, and thyroid hormones linked to reproductive status. Alanine aminotransferase was solely influenced by reproductive status. Urea, vitamins, and certain enzymes exhibited variations with both reproductive status and seasons. The study underscores the importance of considering these factors for accurate serum chemistry interpretation and recommends nutritional supplements during specific periods to mitigate performance decline and economic losses in sheep.
Choi B, Vilahur G, Yadegar D, Viles-Gonzalez J, Badimon JJ. The role of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the prevention and possible treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Curr Mol Med. 2006;6(5):571–587. https://doi.org/10.2174/156652406778018590
Jeppesen J. Triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and risk of ischemic heart disease: a view from the Copenhagen Male Study. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2003;1(1):33–53. https://doi.org/10.1089/154041903321648243
Millán J, Pintó X, Muñoz A, et al. Lipoprotein ratios: physiological significance and clinical usefulness in cardiovascular prevention. Vascul Health Risk Manag. 2009;5:757–765. https://doi.org/10.2147/vhrm.s12187457
Köbrich C, Rehman T, Khan M. Typification of farming systems for constructing representative farm models: two illustrations of the application of multi-variate analyses in Chile and Pakistan. Agricul Syst. 2003;76(1):141–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-521X(02)00013-6
Maroni M, Fanetti AC, Metruccio F. Risk assessment and management of occupational exposure to pesticides in agriculture. La Med del Lavoro. 2006;97(2):430–437.
Rashid S, Rashid W, Tulcan RXS, Huang H. Use, exposure, and environmental impacts of pesticides in Pakistan: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2022;29(29):43675–43689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20164-7
Remor AP, Totti CC, Moreira DA, Dutra GP, Heuser VD, Boeira JM. Occupational exposure of farm workers to pesticides: biochemical parameters and evaluation of genotoxicity. Environ Int. 2009;35(2):273–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2008.06.011
The study in Rio Grande do Sul assessed the impact of pesticide exposure on farm workers. Decreased BChE and ALA-D enzyme activities were observed, suggesting pesticide exposure. While no significant hematological differences were found, the study emphasized the association between pesticide exposure and reduced enzyme activities and increased DNA damage, underscoring the importance of protective measures.
Wafa T, Nadia K, Amel N, et al. Oxidative stress, hematological and biochemical alterations in farmers exposed to pesticides. J Environ Sci Health Part B. 2013;48(12):1058–1069. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2013.824285
Nelson RH. Hyperlipidemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Prim Care. 2013;40(1):195–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pop.2012.11.003
Setiawan B, Darsuni A, Muttaqien F, et al. The effects of combined particulate matter 10 coal dust exposure and high-cholesterol diet on lipid profiles, endothelial damage, and hematopoietic stem cells in rats. J Exper Integ Med. 2013;3(3):219–223.
Freeman D, Griffin B, Murray E, et al. Smoking and plasma lipoproteins in man: effects on low density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and high density lipoprotein subfraction distribution. Eur J Clin Invest. 1993;23(10):630–640. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2362.1993.tb00724.x
Natarajan P, Ray KK, Cannon CP. High-density lipoprotein and coronary heart disease: current and future therapies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55(13):1283–1299.
Solanki JD, Naisargi NH, Mehta HB, Shah CJ. Visual evoked potential: head size, sex, and BMI. Sudan J Ophthalmol. 2013;5(2):79–81. https://doi.org/10.4103/1858-540X.124835
Copyright (c) 2025 Alina Nawaz, kaleem maqsood, farwa liaqat, Naira Nizam, Nabila Roohi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
BSR follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed the Copyright and Author Consent Form.










