Environmental and Genetic Etiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting joints, characterized by pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Through a meticulous evaluation of recent studies, this review explores emerging molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying RA pathogenesis. Although RA is idiopathic, several factors such as environmental influences, diet, the microbiome, gut microbiota, and genetic variations play a significant role in its pathogenesis. The involvement of various genetic factors, including HLA alleles and specific SNPs in genes such as PADI4, REL, RUNX1, FCGR2A, and CD40, has been identified in RA susceptibility. Additionally, the dysregulation of various genetic molecules, such as lncRNAs and miRNAs and proteins including IL-1 and CD28 contributes to inflammation and disease progression. Understanding the disease causing molecular and cellular mechanisms helps to identify therapeutic targets and guide personalized treatment strategies for RA.
Downloads
References
Naqvi A, Hassali M, Aftab M, et al. Development of Evidence-Based Disease Education Literature for Pakistani Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Diseases. 2017;5(4):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases5040027
Giannini D, Antonucci M, Petrelli F, Bilia S, Alessia Alunno, Ilaria Puxeddu. One year in review 2020: pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. 2020;38:387-397. https://doi.org/10.55563/clinexprheumatol/3uj1ng
Radu AF, Bungau SG. Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: an Overview. Cells. 2021;10(11):2857. https://doi. org/10.3390/cells10112857
Carli L, Calabresi E, Governato G, Braun J, Reumatologia. One year in review 2018: axial spondyloarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37:889-898. Accessed February 25, 2025. https://i.clinref.com/data/uploads/articles/axial-spondyloarthritis-one-year-in-review-2018.pdf
Häger J, Bang H, Hagen M, et al. The Role of Dietary Fiber in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Feasibility Study. Nutrients. 2019;11(10). https://doi.org/ 10.3390/nu11102392
Dorji S, Yangchen S, chuki P. Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases visiting the rheumatology clinic at the National Referral Hospital, Bhutan. SAGE Open Medicine. 2024;12. https://doi.org/10.1177/ 20503121231223313
Slowikowski K, Wei K, Brenner MB, Raychaudhuri S. Functional genomics of stromal cells in chronic inflammatory diseases. Current Opinion in Rheumatology. 2018;30(1):65-71. https://doi.org/10. 1097/bor.0000000000000455
Lorenz H, Dalpke AH, Axel Deboben, et al. Mycobacterium kansasii tenosynovitis in a rheumatoid arthritis patient with long‐term therapeutic immunosuppression. Arthritis Care & Research. 2008;59(6):900-903. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.23717
Pati S, Irfan W, Jameel A, Ahmed S, Shahid RK. Obesity and Cancer: a Current Overview of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Outcomes, and Management. Cancers. 2023;15(2):485. https://doi.org/10. 3390/cancers15020485
Metwaly A, Reitmeier S, Haller D. Microbiome risk profiles as biomarkers for inflammatory and metabolic disorders. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 2022;19. https://doi.org/10.1038 /s41575-022-00581-2
Hu Y, Costenbader KH, Gao X, et al. Sugar-sweetened soda consumption and risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis in women. The American journal of clinical nutrition. 2014;100(3):959-967. https://doi.org/ 10.3945/ajcn.114.086918
Tufvesson E, Bozovic G, Hesselstrand R, Bjermer L, Scheja A, Wuttge DM. Increased cysteinyl-leukotrienes and 8-isoprostane in exhaled breath condensate from systemic sclerosis patients. Rheumatology. 2010;49(12):2322-2326. https://doi. org/10.1093/rheumatology/keq271
Tseng CC, Chen SN, Hwang JF, Lin CJ, Chen HS. Progressive outer retinal necrosis associated with occlusive vasculitis in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association. 2012;114(5):469-472. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.jfma.2012.04.005
Weng LH, Ko JY, Wang CJ, Sun YC, Wang FS. Dkk-1 promotes angiogenic responses and cartilage matrix proteinase secretion in synovial fibroblasts from osteoarthritic joints. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 2012;64(10):3267-3277. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.34602
Cox AR, Masschelin PM, Saha PK, et al. The rheumatoid arthritis drug auranofin lowers leptin levels and exerts antidiabetic effects in obese mice. Cell Metabolism. 2022;34(12):1932-1946.e7. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2022.09.019
Ilar A, Gustavsson P, Wiebert P, Alfredsson L. Occupational exposure to organic dusts and risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis: findings from a Swedish population-based case–control study. RMD Open. 2019;5(2):e001049. https://doi.org /10.1136/rmdopen-2019-001049
Poole JA, Thiele GM, K. Janike, et al. Combined Collagen‐Induced Arthritis and Organic Dust‐Induced Airway Inflammation to Model Inflammatory Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 2019;34(9):1733-1743. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.3745
Gianfrancesco MA, Trupin L, Shiboski S, et al. Smoking Is Associated with Higher Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Longitudinal Study Controlling for Time-varying Covariates. The Journal of Rheumatology. 2018;46(4):370-375. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.180262
Seror R, Henry J, Gusto G, Aubin HJ, Boutron-Ruault MC, Mariette X. Passive smoking in childhood increases the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2018;58(7):1154-1162. https://doi.org/ 10.1093/rheumatology/key219
Karlson EW, Chang S-C, Cui J, et al. Gene–environment interaction between HLA-DRB1 shared epitope and heavy cigarette smoking in predicting incident rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2009;69(01):54-60. https:// doi.org/10.1136/ard.2008.102962
Ishikawa Y, Ikari K, Hashimoto M, et al. Shared epitope defines distinct associations of cigarette smoking with levels of anticitrullinated protein antibody and rheumatoid factor. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2019;78(11):1480-1487. https://doi. org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215463
Murphy MP, Hunt D, Herron M, et al. Neutrophil-Derived Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase Activity Contributes to Pulmonary Emphysema by Enhancing Elastin Degradation. The Journal of Immunology. 2024;213(1):75-85. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.2300658
Cheng L, Qian L, Xu ZZ, Tan Y, Luo CY. Aromatic hydrocarbon receptor provides a link between smoking and rheumatoid arthritis in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. PubMed. 2018;37(3):445-449.
Regueiro C, Rodriguez-Rodriguez L, Lopez-Mejias R, et al. A predominant involvement of the triple seropositive patients and others with rheumatoid factor in the association of smoking with rheumatoid arthritis. Scientific Reports. 2020;10(1). https://doi.org /10.1038/s41598-020-60305-x
Kronzer VL, Crowson CS, Sparks JA, Vassallo R, Davis JM. Investigating Asthma, Allergic Disease, Passive Smoke Exposure, and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatology. 2019;71(8):1217-1224. https://doi.org/10.1002/art. 40858
Yao Y, Cai X, Fei W, et al. Regulating Gut Microbiome: Therapeutic Strategy for Rheumatoid Arthritis During Pregnancy and Lactation. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 2020;11:594042. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.594042
Rosser EC, Piper CJM, Matei DE, et al. Microbiota-Derived Metabolites Suppress Arthritis by Amplifying Aryl-Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation in Regulatory B Cells. Cell Metabolism. 2020;31(4):837-851.e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.03.003
Tajik N, Frech M, Schulz O, et al. Targeting zonulin and intestinal epithelial barrier function to prevent onset of arthritis. Nature Communications. 2020;11(1). https:// doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15831-7
Song Y, Li J, Wu Y. Evolving understanding of autoimmune mechanisms and new therapeutic strategies of autoimmune disorders. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. 2024;9(1). https://doi.org /10.1038/s41392-024-01952-8
Kochi Y, Suzuki A, Yamada R, Yamamoto K. Ethnogenetic heterogeneity of rheumatoid arthritis—implications for pathogenesis. Nature Reviews Rheumatology. 2010;6(5):290-295. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2010.23
YAMAMOTO K, OKADA Y, SUZUKI A, KOCHI Y. Genetic studies of rheumatoid arthritis. Proceedings of the Japan Academy, Series B. 2015;91(8):410-422. https://doi.org/10.2183/pjab.91.410
Vetchinkina EA, Mikhaylenko DS, Kuznetsova EB, et al. Genetic Factors of Predisposition and Clinical Characteristics of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Russian Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021;11(6):469. https://doi.org/10. 3390/jpm11060469
Regueiro C, Desiré Casares-Marfil, Lundberg K, et al. HLA–B*08 Identified as the Most Prominently Associated Major Histocompatibility Complex Locus for Anti–Carbamylated Protein Antibody–Positive/Anti–Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide–Negative Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis & rheumatology. 2021;73(6):963-969. https://doi.org /10.1002/art.41630
Mansouri P, Mansouri P, Behmard E, Najafipour S, Kouhpayeh SA, Farjadfar A. Peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD): A promising target for chronic diseases treatment. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2024;73(6):134576-134576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. ijbiomac.2024.134576
35. Coenen D, Verschueren P, Westhovens R, Bossuyt X. Technical and Diagnostic Performance of 6 Assays for the Measurement of Citrullinated Protein/Peptide Antibodies in the Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clinical Chemistry. 2007;53(3):498-504. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2006.078063
Goldbach-Mansky R, Lee J, McCoy A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis associated autoantibodies in patients with synovitis of recent onset. Arthritis Research. 2000;2(3):236-243. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar93
Chang X, Xia Y, Pan J, Meng Q, Zhao Y, Yan X. PADI2 is significantly associated with rheumatoid arthritis. PloS One. 2013;8(12):e81259. https:// doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0081259
Perricone C, Ceccarelli F, Valesini G. An overview on the genetic of rheumatoid arthritis: A never-ending story. Autoimmunity Reviews. 2011;10(10):599-608. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.autrev.2011.04.021
Baños-Hernández CJ, Navarro-Zarza JE, Parra-Rojas I, et al. PADI4 polymorphisms and the functional haplotype are associated with increased rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility: A replication study in a Southern Mexican population. Human Immunology. 2017;78(9):553-558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2017.05.005
Li J, Mahajan A, Tsai MD. Ankyrin Repeat: A Unique Motif Mediating Protein−Protein Interactions. Biochemistry. 2006;45(51):15168-15178. https://doi.org/10.1021/ bi062188q
Ruiz-Perera LM, Greiner JFW, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B. A Matter of Choice: Inhibition of c-Rel Shifts Neuronal to Oligodendroglial Fate in Human Stem Cells. Cells. 2020;9(4):1037. https://doi.org/10. 3390/cells9041037
Gilmore TD, Kalaitzidis D, Liang MC, Starczynowski DT. The c-Rel transcription factor and B-cell proliferation: a deal with the devil. Oncogene. 2004;23(13):2275-2286. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207410
Salah E, Ahmed AA. A new piece of an old puzzle: lack of association between C-Rel (rs13031237-rs842647) single nucleotide polymorphisms and non-segmental vitiligo. Biomedical Dermatology. 2018;2(1). https://doi.org/10.1186 /s41702-018-0027-6
Ann Sanoji Samarakkody, Shin NY, Cantor AB. Role of RUNX Family Transcription Factors in DNA Damage Response. PubMed. 2020;43(2):99-106. https://doi.org/10.14348/ molcells.2019.0304
Farzana Yasmeen, Rameez Hassan Pirzada, Ahmad B, Choi B, Choi S. Understanding Autoimmunity: Mechanisms, Predisposing Factors, and Cytokine Therapies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024;25(14):7666-7666. https://doi. org/10.3390/ijms25147666
Dingwall HL. Developmental Genetics and the Evolution of Tendon Growth - ProQuest. Proquest.com. Published 2019. Accessed February 25, 2025. https://www.proquest.com/ openview/7dfa45728f0da12b28db04dd7a7c9fba/1?pq-origsite=gscholar& cbl=18750&diss=y
Pandey JP. Genomewide Association Studies and Assessment of Risk of Disease. New England Journal of Medicine. 2010;363(21):2076-2077. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmc1010310
Fierabracci A, Arena A, Toto F, et al. Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 (APECED) in the Indian population: case report and review of a series of 45 patients. Journal of endocrinological investigation. 2021;44(4):661-677. https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s40618-020-01376-5
Yang Y, Peng L, He C, et al. The role of genetic variants in FCGR2A on the risk of rheumatoid arthritis in the Han Chinese population. Research Square (Research Square). Published online September 2, 2020. https:// doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-63617/v1
Anderson MS, Su MA. AIRE expands: new roles in immune tolerance and beyond. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2016;16(4):247-258. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.9
Chen J, Zhang A, Yang Y, Si Y, Hao D. Assessment of interleukin 6 gene polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis. Gene. 2020;765:145070-145070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene .2020.145070
Liu X, Peng L, Li D, et al. The Impacts of IL1R1 and IL1R2 Genetic Variants on Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk in the Chinese Han Population: A Case–Control Study. International Journal of General Medicine. 2021;Volume 14:2147-2159. https://doi.org/10. 2147/ijgm.s291395
Xie Q, Xu WD, Pan M, et al. Association of IL-35 expression and gene polymorphisms in rheumatoid arthritis. International immunopharmacology. 2021; 90:107231-107231. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107231
Hu Z, Zhang L, Lin Z, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis patients from South China: modeled by three methods. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2021;22(1). https://doi.org/ 10.1186/s12891-021-04403-5
Matsui T, Connolly JE, Michnevitz M, et al. CD2 Distinguishes Two Subsets of Human Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells with Distinct Phenotype and Functions. Journal of Immunology. 2009;182(11):6815-6823. https://doi.org/10.4049/ jimmunol.0802008
Binder C, Cvetkovski F, Sellberg F, et al. CD2 Immunobiology. Frontiers in Immunology. 2020;11. https://doi.org /10.3389/fimmu.2020.01090
Huang Q, Xu WD, Su LC, Liu XY, Huang AF. Association of CD40 Gene Polymorphisms With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Chinese Han Population. Frontiers in Immunology. 2021;12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.642929
Chan HC, Wang SC, Lin CH, Lin YZ, Li RN, Yen JH. A novel CD209 polymorphism is associated with rheumatoid arthritis patients in Taiwan. Frontiers in Immunology. 2021;35(5).https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.23751
Podgórska D, Cieśla M, Majdan M, Podgórski R, Kolarz B. The relationship of ADAMTSL2 and LRPAP1 gene methylation level with rheumatoid arthritis activity. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. Published online August 4, 2021. https://doi.org/10.55563/clinexprheumatol/ogk9sd
Doody KM, Bottini N, Firestein GS. Epigenetic alterations in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Epigenomics. 2017;9(4):479-492. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi-2016-0151
Kolarz B, Podgorska D, Podgorski R. Insights of rheumatoid arthritis biomarkers. Biomarkers. Published online July 14, 2020:1-34. https://doi.org/10.1080/1354750x.2020.1794043
62. Nemtsova MV, Zaletaev DV, Bure IV, et al. Epigenetic Changes in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Frontiers in Genetics. 2019;10(570). https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00570
Moore LD, Le T, Fan G. DNA Methylation and Its Basic Function. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;38(1):23-38. https://doi.org/10. 1038/npp.2012.112
Klein K, Gay S. Epigenetic modifications in rheumatoid arthritis, a review. Current Opinion in Pharmacology. 2013;13(3):420-425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2013.01.007
Zheng F, Yu X, Huang J, Dai Y. Circular RNA expression profiles of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients, based on microarray chip technology. Molecular Medicine Reports. 2017;16(6):8029-8036. https://doi.org /10.3892/mmr.2017.7638
Luo Z, Chen S, Chen X. CircMAPK9 promotes the progression of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis via the miR-140-3p/PPM1A axis. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research. 2021;16(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-021-02550-y
Renman E, Brink M, Ärlestig L, Solbritt Rantapää-Dahlqvist, Lejon K. Dysregulated microRNA expression in rheumatoid arthritis families—a comparison between rheumatoid arthritis patients, their first-degree relatives, and healthy controls. Clinical Rheumatology. 2020;40(6):2387-2394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05502-9
Cieśla M, Kolarz B, Majdan M, Darmochwał-Kolarz D. Plasma micro-RNA-22 is associated with disease activity in well-established rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. 2021;40(5). https://doi.org/10.55563/clinexprheumatol/zdhkrp
Zhao Y, Vartak SV, Conte A, et al. “Stripe” transcription factors provide accessibility to co-binding partners in mammalian genomes. Molecular Cell. 2022;82(18):3398-3411.e11. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2022.06.029
Li G, Liu Y, Meng F, et al. Tanshinone IIA promotes the apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by up-regulating lncRNA GAS5. Bioscience Reports. 2018;38(5). https://doi.org/10. 1042/bsr20180626
Jiang H, Fan C, Lu Y, Cui X, Liu J. Astragaloside regulates lncRNA LOC100912373 and the miR 17 5p/PDK1 axis to inhibit the proliferation of fibroblast like synoviocytes in rats with rheumatoid arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Medicine. 2021;48(1). https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2021.4963
Zhang J, Lei H, Li X. LncRNA SNHG14 contributes to proinflammatory cytokine production in rheumatoid arthritis via the regulation of the miR-17-5p/MINK1-JNK pathway. Environmental Toxicology. 2021;36(12):2484-2492. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.23361
Liu C, Guo X, Bai S, Zeng G, Wang H. lncRNA CASC2 downregulation participates in rheumatoid arthritis, and CASC2 overexpression promotes the apoptosis of fibroblast like synoviocytes by downregulating IL 17. Molecular Medicine Reports. 2020;21. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr. 2020.11018
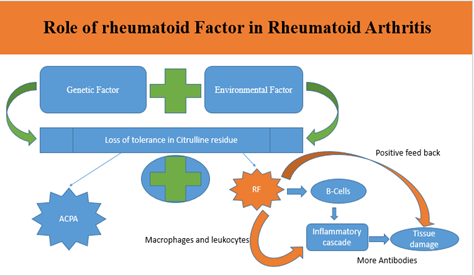
Copyright (c) 2025 Fazal Shan, Muhammad Ibrahim Rashid, Shah Faisal Jamal, Irshad Ahmad

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
BSR follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed the Copyright and Author Consent Form.










