Clinical Characteristics, Causes, and Treatment Outcomes of Hydrocephalus in Children Under Six: A Retrospective Study from a Single Center in Quetta, Baluchistan
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
Background. Hydrocephalus is defined by an abnormal build-up of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) within the brain's ventricles. The long-term effects of hydrocephalus can range considerably and are frequently unpredictable. Due to its life-threatening nature, particularly in newborns and toddlers, the treatment of hydrocephalus is of utmost importance. The exact epidemiology of infantile hydrocephalus in Pakistan is unknown. \
Methods. This retrospective cohort study intended to examine the clinical importance of hydrocephalus patients under 6 years. Furthermore, it also addressed the potential gaps in medical knowledge on the local epidemiology, risk factors, and therapeutic methods of this condition at a tertiary care centre of Quetta Baluchistan, Pakistan.
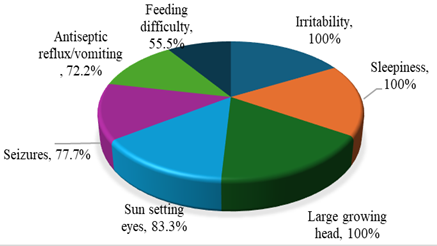
Results. A total of 29 hydrocephalus patients (18 congenital and 11acquired) were included in the study. A comprehensive questionnaire was designed to collect the demographic and clinical information of the patients. After statistical analysis, it was determined that gender and age distribution between the two groups, congenital and acquired hydrocephalus, was similar, showing no significant differences (p=0.196, p=0.867). The most common symptoms were irritability, drowsiness, and a head growing through seizures. Moreover, sun-setting eyes also appeared commonly. Post-natal diagnosis and imaging (CT and MRI) dominated the diagnostic methods of congenital hydrocephalus. Whereas brain MRI accounted for most cases with acquired hydrocephalus. The origin of acquired hydrocephalus was frequently unknown, aqueduct stenosis was the primary cause of congenital hydrocephalus. Medical treatment, ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunting, and ETV (Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy) were similar in all groups. The most frequent side effect for medications and VP shunts was irritation, while the most frequent side effect for ETV operations was sore throat.
Conclusion. This study underlined the importance of early diagnosis, proper treatment, and continuous follow-up in hydrocephalus patients. Though the treatment approaches in accordance with clinical practices, the frequency of complications has necessitated continued medical care to achieve the best possible outcomes. Further research into the local epidemiology and more effective therapeutic approaches is very important to enhance care for hydrocephalus patients in the region.
Downloads
References
Hetherington R, Dennis M, Barnes M, Drake J, Gentili F. Functional outcome in young adults with spina bifida and hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv Syst. Feb 2006;22(2):117-24. https://doi.org/10 .1007/s00381-005-1231-4
Kahle KT, Kulkarni AV, Limbrick DD, Warf BC. Hydrocephalus in children. The lancet. 2016;387(10020):788-799.
Tully HM, Dobyns WB. Infantile hydrocephalus: a review of epidemiology, classification and causes. European journal of medical genetics. 2014;57(8):359-368. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmg.2014.06.002
Surti A, Usmani A, Javaid Q, Shafique S. Association of fetal hydrocephalus with other embryological anomalies: A prenatal ultrasound-based study. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences. 2022;38(6):1617. https://doi.org/10. 12669/pjms.38.6.5223
Alhassan A, Adam A, Nangkuu D. Prevalence of neural tube defect and hydrocephalus in Northern Ghana. Journal of Medical and Biomedical Sciences. 2017;6(1):18-23. https://doi. org/10.4314/jmbs.v6i1.3
Dewan MC, Rattani A, Mekary R, et al. Global hydrocephalus epidemiology and incidence: systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of neurosurgery. 2018;130(4):1065-1079. https://doi. org/10.3171/2017.10.JNS17439
Khan A, Zuhaid M, Fayaz M, et al. Frequency of congenital anomalies in newborns and its relation to maternal health in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Peshawar, Pakistan. International Journal of Medical Students. 2015;3(1):19-23. https://doi.org/10. 5195/ijms.2015.108
Kirkpatrick M, Engleman H, Minns R. Symptoms and signs of progressive hydrocephalus. Archives of disease in childhood. 1989;64(1):124-128.
Quencer RM. Intracranial CSF flow in pediatric hydrocephalus: evaluation with cine-MR imaging. American journal of neuroradiology. 1992;13(2):601-608. http://www.ajnr. org/content/13/2/601
Faggin R, CalDeRone M, Denaro L, Meneghini L, d'Avella D. Long-term operative failure of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in pediatric patients: the role of cine phase-contrast MR imaging. Neurosurgical Focus. 2011;30(4):E1. https://doi.org/10. 3171/2011.1.FOCUS10303
Adeloye A. Management of infantile hydrocephalus in Central Africa. Tropical doctor. 2001;31(2):67-70. https://doi.org/10.1177/004947550103100203
Kiefer M, Unterberg A. The differential diagnosis and treatment of normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. 2012;109(1-2):15. https://doi.org/10. 3238/arztebl.2012.0015
Kanev PM, Park T. The treatment of hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery Clinics of North America. 1993;4(4):611-619. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1042-3680 (18)30553-9
Vinchon M, Rekate H, Kulkarni AV. Pediatric hydrocephalus outcomes: a review. Fluids and Barriers of the CNS. 2012;9(1):1-10. https://doi.org /10.1186/2045-8118-9-18
Pan P. Outcome analysis of ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery in pediatric hydrocephalus. Journal of Pediatric Neurosciences. 2018;13(2):176.https://doi.org/10.4103/jpn.jpn_29_18
Kyalo MC, Nganga NH, Kamau MN. Management and functional outcome of childhood hydrocephalus at the kenyatta national hospital, nairobi. 2015.
Tambo FM, Djientcheu V, Chiabi A, et al. Our experience in the management of infantile hydrocephalus: a study on thirty-five regrouped cases in Yaounde, Cameroon. African Journal of Paediatric Surgery. 2011;8(2):199. https://doi.org/10.4103/0189-6725. 86062
Abebe MS, Seyoum G, Emamu B, Teshome D. Congenital Hydrocephalus and Associated Risk Factors: An Institution-Based Case–Control Study, Dessie Town, North East Ethiopia. Pediatric Health, Medicine and Therapeutics. 2022; 13:175-182. https://doi.org/10.2147/phmt.s364447
Kutscher A, Nestler U, Bernhard MK, et al. Adult long-term health-related quality of life of congenital hydrocephalus patients. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics. 2015;16(6):621-625. https://doi.org/ 10.3171/2015.4.PEDS15106
Yusuf AS, Omokanye HK, Adeleke NA, Akanbi RO, Ajiboye SO, Ibrahim HG. Management and outcome of infantile hydrocephalus in a tertiary health institution in Nigeria. Journal of Neurosciences in Rural Practice. 2017;8(02):249-253. https://doi.org/ 10.4103/jnrp.jnrp_321_16
Ahmed A, Sandlas G, Kothari P, et al. Outcome analysis of shunt surgery in hydrocephalus. Journal of Indian Association of Pediatric Surgeons. 2009;14(3):98. https://doi.org/10. 4103/0971-9261.57700
Shallat RF, Pawl RP, Jerva MJ. Significance of upward gaze palsy (Parinaud's syndrome) in hydrocephalus due to shunt malfunction. Journal of neurosurgery. 1973;38(6):717-721. https://doi.org/ 10.3171/jns.1973.38.6.0717
Saidu SA, Maaji SM, Nzeh DA, Shehu B, Ismail N. Sonographic pattern of hydrocephalus among the under five children in Sokoto North Western Nigeria. Sahel Medical Journal. 2015;18(4):172-172. https://doi.org/ 10.4103/1118-8561.176584
Moritake K, Nagai H, Nagasako N, Yamasaki M, Oi S, Hata T. Diagnosis of congenital hydrocephalus and delivery of its patients in Japan. Brain and Development. 2008;30(6):381-386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. braindev.2007.11.002
Luscombe NM, Greenbaum D, Gerstein M. What is bioinformatics? A proposed definition and overview of the field. Methods of information in medicine. 2001;40(04):346-358. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1634431
Hetherington R, Dennis M, Barnes M, Drake J, Gentili F. Functional outcome in young adults with spina bifida and hydrocephalus. Child’s Nervous System. 2005;22(2):117-124. https:// doi.org/10.1007/s00381-005-1231-4
Deshmukh SN, Yadav AT. Clinical study and management of hydrocephalus in children. International Surgery Journal. 2020;7(4):1258-1262. https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s00381-011-1527-5
Mancao M, Miller C, Cochrane B, Hoff C, Sauter K, Weber E. Cerebrospinal fluid shunt infections in infants and children in Mobile, Alabama. Acta Paediatrica. 2007;87(6):667-670. https://doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1998.tb01527.x
Rajshekhar V, Moorthy R. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy for hydrocephalus: A review of indications, outcomes, and complications. Neurology India. 2011;59(6):848.https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.91364
Javadpour M, Mallucci C, Brodbelt A, Golash A, May P. The impact of endoscopic third ventriculostomy on the management of newly diagnosed hydrocephalus in infants. Pediatric neurosurgery. 2001;35(3):131-135. https://doi.org/10.1159/000050406
Copyright (c) 2025 Nadia Ewaz Ali, Humera Javed, Bibi Asma, Samia Ishtiaq, Saira Iqbal, Nabeela Tariq

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
BSR follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed the Copyright and Author Consent Form.










