Effects of Hepatitis on Diabetic Profile, Renal Function, and Hematological Factors in HCV Positive Patients Diagnosed via Real-Time PCR
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
Background. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a blood-borne infection that has spread all over the world. Around 10 million people in Pakistan are impacted by HCV, while over 58 million people worldwide have a chronic HCV infection. HCV is well known for its severe effects on the liver as well as its extra-hepatic manifestations.
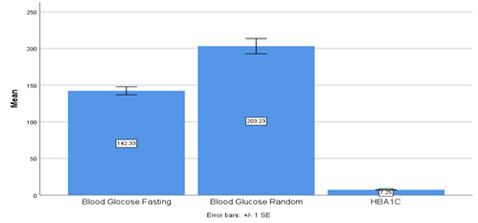
Objective. This study assessed the renal profile (urea and creatinine), hematological factors (Hb, HCT, MCV), and diabetic profile (blood glucose fasting, blood glucose random, and HbA1c) of HCV-positive patients confirmed by real-time PCR (RT-PCR). The main aim was to determine the impact of hepatitis infection.
Methodology. This was a retrospective cohort study conducted on patients diagnosed as HCV-positive by using real-time PCR (RT-PCR). Their diabetic, renal, and hematological association with HCV was observed and analyzed by using SPSS 25.
Results. Out of 296 HCV-positive patients, 174 (58.8%) were male and 122 (41.2%) were female, indicating that HCV was found to be more prevalent in male patients. There was no statistical association found between HbA1c and gender. However, there was found a significant association of blood glucose fasting and blood glucose random with gender. Renal and hematological profiles were also disturbed in HCV-infected individuals.
Conclusion. Health professionals may benefit from this study by managing disrupted profiles more effectively and providing improved patient care. Additional research on the disrupted hematological, renal, and diabetic profiles may improve the treatment conditions for patients since these profiles revealed a variety of extra-hepatic symptoms in this study
Downloads
References
Kaplan DE. Hepatitis C virus. Ann Int Med. 2020;173(5):ITC33–ITC48. https://doi.org/10.7326/AITC202009010
Roger S, Ducancelle A, Le Guillou-Guillemette H, Gaudy C, Lunel F. HCV virology and diagnosis. Clinics Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2021;45(3):e101626. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.clinre.2021.101626
Masia R, Misdraji J. Liver and bile duct infections. Diagnost Pathol Infect Dis. 2018:272–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-44585-6.00011-4
Guntipalli P, Pakala R, Gara SK, et al. Worldwide prevalence, genotype distribution and management of hepatitis C. Acta Gastro Belg. 2021;84(4):637–656.
Mooneyhan E, Qureshi H, Mahmood H, et al. Hepatitis C prevalence and elimination planning in Pakistan, a bottom‐up approach accounting for provincial variation. J Viral Hepatitis. 2023;30(4):345–354. https://doi.org/ 10.1111/jvh.13802
Arshad A, Ashfaq UA. Epidemiology of hepatitis C infection in Pakistan: current estimate and major risk factors. Critic Rev in Eukaryotic Gene Expr. 2017;27(1):63–77. https://doi.org/ 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2017018953
Negro F. Natural history of hepatic and extrahepatic hepatitis C virus diseases and impact of interferon-free HCV therapy. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Med. 2020;10(4):ea036921. https:// doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a036921
Chakraborty AK, Swapnil MAM, Al Mamun A, Karim F, Dey U. Association of Biochemical Markers between Hepatitis C Virus and Diabetes Mellitus among Bangladeshi Male. Insight. 2022;5(01):190–197.
Henson JB, Sise ME. The association of hepatitis C infection with the onset of CKD and progression into ESRD. Seminars Dialysis. 2019;32(2):108–118. https://doi.org/10.1111/sdi.12759
Asaduzzaman M, Bappy SR, Fatema B, et al. Effect of hepatitis C virus (HCV) on hemoglobin, blood cells and random blood glucose levels among serologically positive HCV patients. IOSR J Nurs Health Sci. 2017;6(5):41–45.
Takei F, Tani H, Matsuura Y, Nakatani K. Detection of hepatitis C virus by single-step hairpin primer RT-PCR. Bioorg Med Chem Letters. 2014;24(1):394–396. https://doi.org /10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.10.021
Abdel-Gawad M, Nour M, El-Raey F, Nagdy H, Almansoury Y, El-Kassas M. Gender differences in prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in Egypt: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):e2499. https:// doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-29262-z
Fabiani S, Fallahi P, Ferrari SM, Miccoli M, Antonelli A. Hepatitis C virus infection and development of type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Rev Endocr Metabol Disord. 2018;19:405–420. https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s11154-017-9440-1
Chaudhury CS, Sheehan J, Chairez C, et al. No improvement in hemoglobin A1c following hepatitis C viral clearance in patients with and without HIV. J Infect Dis. 2018;217(1):47–50. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jix517
Roccatello D, Fornasieri A, Giachino O, et al. Multicenter study on hepatitis C virus–related cryoglobulinemic glomerulonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;49(1):69–82. https://doi.org/ 10.1053/j.ajkd.2006.09.015
Rasheed H, Khawar MB, Sohail AM, et al. Altered hematological parameters in HCV infection: a diagnostic approach. Asian J Health Sci. 2022;8(2):eID46.
Guo F, Moellering DR, Garvey WT. Use of HbA1c for diagnoses of diabetes and prediabetes: comparison with diagnoses based on fasting and 2-hr glucose values and effects of gender, race, and age. Metabol Synd Relat Disord. 2014;12(5):258–268. https://doi.org/10.1089/met.2013.0128
Negro F, Alaei M. Hepatitis C virus and type 2 diabetes. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(13):1537–1547. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg. 15.1537
Bhattacharya D, Aronsohn A, Price J, Lo Re V. Clinical practice guidance for testing, managing, and treating Hepatitis C virus infection: 2023 Update by AASLD-IDSA. Clinic Infect Dis. 2023:eciad319. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciad319
Lam L, Fontaine H, Lapidus N, et al. Impact of direct‐acting antiviral treatment for hepatitis C on cardiovascular diseases and extrahepatic cancers. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Safety. 2023;32(4):486–495. https://doi.org/10.1002/pds.5576
Copyright (c) 2025 Tahira Batool, Tahira Idrees, Rukhsar Akbar, Rabbia Mutaqeen, Asma Irshad

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
BSR follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed the Copyright and Author Consent Form.










