Investigating the Anti-Tubercular Potential of Novel Non-Antibiotic Agents against Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
Background. The ever-increasing prevalence of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MDR-TB) presents an alarming challenge to existing tuberculosis (TB) treatment stratgies. Hence, the current study explores the potential of dihydroergotamine and abiraterone acetate, two non-antibiotic compounds, as innovative anti-tubercular agents.
Methods. In silico analyses were conducted to identify potential drug targets for dihydroergotamine and abiraterone acetate. Subsequently, these compounds were evaluated for their bactericidal efficacy against both the reference H37Rv strain and an MDR-TB strain of M. tuberculosis in vitro. A range of drug concentrations were tested to determine their inhibitory effects.
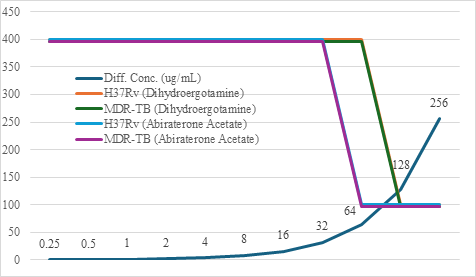
Results. Both dihydroergotamine and abiraterone acetate exhibited substantial inhibitory activity against M. tuberculosis. Dihydroergotamine demonstrated efficacy at higher concentrations (128 µg and 256 µg), while abiraterone acetate exhibited potency at lower concentrations (64 µg, 128 µg, and 256 µg). The observed dose-dependent inhibitory effect emphasizes the importance of optimizing drug concentrations in anti-tubercular therapy.
Conclusion. Both compounds act as potential anti-tubercular agents by effectively inhibiting the growth of M. tuberculosis, with abiraterone acetate demonstrating greater potency at lower concentrations. These findings suggest both compounds may be promising candidates for further research and development as potential treatments for tuberculosis.
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2024 Muhammad Fayaz Khan, Abdul Jabbar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
BSR follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed the Copyright and Author Consent Form.










