Development of Microbial Biofilms and Their Role in device, non-device and organ system level Infections
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
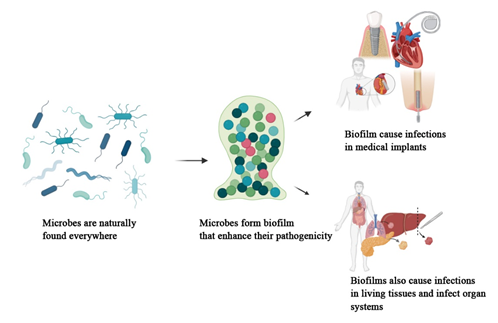
Background. Microorganisms, while providing many health benefits to human beings and other living organisms, are also responsible for significant infections. They cause infections in both planktonic and biofilm modes. Biofilms, defined as architectural communities of microorganisms encased in an extracellular polymeric substance (EPS), are strongly associated with infections. According to the National Institute of Health Sciences (NIH), biofilms account for 65% of microbial infections and 80% of chronic infections.
Methods. This review examines the current literature on microbial biofilms, focusing on their formation stages, pathogenicity, resistance mechanisms, and associated infections. Data from various studies is analyzed to summarize biofilm development and its role in chronic infections.
Results. Biofilm development involves four stages: attachment, microcolony formation, maturation, and dispersion. Quorum sensing (QS) mechanisms play a critical role in biofilm development and microbial communication. Biofilms enhance microbial pathogenicity and resistance to both the immune system and commercial antibiotics. They contribute to device-associated infections, such as those in catheters, and also to non-device infections in living tissues, as well as organ-level infections that impair systemic functions.
Conclusion. A comprehensive understanding of microbial biofilms is essential for developing strategies to manage and control biofilm-associated infections. This review highlights the need for further research on the mechanisms of biofilm formation and resistance to improve infection prevention and treatment.
Keywords: biofilm development, biofilm infections, chronic infections, device infections, microbial biofilms, non-device infections
Downloads
References
Penesyan A, Paulsen IT, Kjelleberg S, Gillings MR. Three faces of biofilms: a microbial lifestyle, a nascent multicellular organism, and an incubator for diversity. NPJ Biofilms Microb. 2021;7(1):e80. https://doi.org /10.1038/s41522-021-00251-2
Sharma S, Mohler J, Mahajan SD, Schwartz SA, Bruggemann L, Aalinkeel R. Microbial biofilm: a review on formation, infection, antibiotic resistance, control measures, and innovative treatment. Microorganisms. 2023;11(6):e1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061614
Shineh G, Mobaraki M, Bappy MJP, Mills DK. Biofilm formation, and related impacts on healthcare, food processing and packaging, industrial manufacturing, marine industries, and sanitation–a review. Appl Microbiol. 2023;3(3):629–665. https://doi.org/10. 3390/applmicrobiol3030044
Shree P, Singh CK, Sodhi KK, Surya JN, Singh DK. Biofilms:understanding the structure and contribution towards bacterial resistance in antibiotics. Med Microecol. 2023;16:e100084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medmic.2023.100084
Mirzaei R, Mohammadzadeh R, Alikhani MY, et al. The biofilm-associated bacterial infections unrelated to indwelling devices. IUBMB Life. 2020;72(7):1271–1285. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.2266
Vestby LK, Grønseth T, Simm R, Nesse LL. Bacterial biofilm and its role in the pathogenesis of disease. Antibiotics. 2020;9(2):e59. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020059
Brinkman CL, Schmidt-Malan SM, Karau MJ, et al. Exposure of bacterial biofilms to electrical current leads to cell death mediated in part by reactive oxygen species. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0168595. https://doi.org /10.1371/journal.pone.0168595
Liu X, Yao H, Zhao X, Ge C. Biofilm formation and control of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Molecules. 2023;28(6):e2432. https://doi.org/10. 3390/molecules28062432
Sauer K, Stoodley P, Goeres DM, et al. The biofilm life cycle: expanding the conceptual model of biofilm formation. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022;20(10):608–620. https://doi.org/ 10.1038/s41579-022-00767-0
Liaqat I, Muhammad N, Ara C, et al. Bioremediation of heavy metals polluted environment and decolourization of black liquor using microbial biofilms. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(5):3985–3997. https://doi.org /10.1007/s11033-023-08334-3
Abera GB, Trømborg E, Solli L, et al. Biofilm application for anaerobic digestion: a systematic review and an industrial scale case. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024;17(1):e145. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-024-02592-4
Rasamiravaka T, Labtani Q, Duez P, El Jaziri M. The formation of biofilms by pseudomonas aeruginosa: a review of the natural and synthetic compounds interfering with control mechanisms. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015(1):e759348. https://doi. org/10.1155/2015/759348
Armbruster CR, Parsek MR. New insight into the early stages of biofilm formation. PNAS 2018;115(17):4317–4319. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas. 1804084115
Rabin N, Zheng Y, Opoku-Temeng C, Du Y, Bonsu E, Sintim HO. Biofilm formation mechanisms and targets for developing antibiofilm agents. Future Med Chem. 2015;7(4):493–512. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.15.6
Lu L, Zhao Y, Li M, et al. Contemporary strategies and approaches for characterizing composition and enhancing biofilm penetration targeting bacterial extracellular polymeric substances. J Pharm Anal. 2024;14(4):e100906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2023.11.013
Costerton W, Veeh R, Shirtliff M, Pasmore M, Post C, Ehrlich G. The application of biofilm science to the study and control of chronic bacterial infections. J Clin Invest. 2003;112(10):1466–1477. https://doi. org/10.1172/jci20365
Samrot AV, Mohamed AA, Faradjeva E, et al. Mechanisms and impact of biofilms and targeting of biofilms using bioactive compounds-a review. Medicina. 2021;57(8):e839. https:// doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080839
Zhao A, Sun J, Liu Y. Understanding bacterial biofilms: From definition to treatment strategies. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023;13:e1137947. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2023.1137947
He Z, Liang J, Tang Z, Ma R, Peng H, Huang Z. Role of the luxS gene in initial biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;25(1):60–68. https://doi.org/10.1159/000371816
Laganenka L, Sourjik V. Bacterial quorum sensing signals at the interdomain interface. Isr J Chem. 2023;63(5-6):e202200080. https://doi. org/10.1002/ijch.202200080
Brackman G, Cos P, Maes L, Nelis HJ, Coenye T. Quorum sensing inhibitors increase the susceptibility of bacterial biofilms to antibiotics in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55(6):2655–2661. https://doi.org /10.1128/aac.00045-11
Ali A, Zahra A, Kamthan M, et al. Microbial biofilms: applications, clinical consequences, and alternative therapies. Microorganisms. 2023;11(8):e1934. https://doi.org/10. 3390/microorganisms11081934
Chambers HF, Bayer AS. Native-valve infective endocarditis. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(6):567–576. https://doi.org/ 10.1056/NEJMcp2000400
Kaushik A, Kest H, Sood M, Steussy BW, Thieman C, Gupta S. Biofilm producing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections in humans: clinical implications and management. Pathogens. 2024;13(1):e76. https:// doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13010076
Mirghani R, Saba T, Khaliq H, et al. Biofilms: formation, drug resistance and alternatives to conventional approaches. AIMS Microbiol. 2022;8(3):239–277. https://doi.org/ 10.3934/microbiol.2022019
Szczotka-Flynn LB, Pearlman E, Ghannoum M. Microbial contamination of contact lenses, lens care solutions, and their accessories: a literature review. Eye Cont Lens. 2010;36(2):116–129. https://doi.org/ 10.1097/ICL.0b013e3181d20cae
Wu YT, Zhu H, Harmis NY, Iskandar SY, Willcox M, Stapleton F. Profile and frequency of microbial contamination of contact lens cases. Optom Vis Sci. 2010;87(3):E152-E158. https://doi.org/10.1097/opx. 0b013e3181cf86ee
Ayush PT, Ko J-H, Oh H-S. Characteristics of initial attachment and biofilm formation of pseudomonas aeruginosa on microplastic surfaces. Appl Sci. 2022;12(10):e5245. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105245
Gominet M, Compain F, Beloin C, Lebeaux D. Central venous catheters and biofilms: where do we stand in 2017? Apmis. 2017;125(4):365–375. https://doi.org/10.1111/apm.12665
de Sousa T, Hébraud M, Alves O, et al. Study of antimicrobial resistance, biofilm formation, and motility of pseudomonas aeruginosa derived from urine samples. Microorganisms. 2023;11(5):e1345. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/microorganisms11051345
Galar A, Weil AA, Dudzinski DM, Muñoz P, Siedner MJ. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic valve endocarditis: pathophysiology, epidemiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and management. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019;32(2):e00041-18. https://doi.org/ 10.1128/cmr.00041-18
Su Y, Yrastorza JT, Matis M, et al. Biofilms: formation, research models, potential targets, and methods for prevention and treatment. Adv Sci. 2022;9(29):e2203291. https://doi.org/ 10.1002/advs.202203291
Abdel‐Aleem H, Aboelnasr MF, Jayousi TM, Habib FA. Indwelling bladder catheterisation as part of intraoperative and postoperative care for caesarean section. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;2014(4):eCd010322. https://doi. org/10.1002/14651858.CD010322.pub2
Yi-Te C, Shigemura K, Nishimoto K, et al. Urinary tract infection pathogens and antimicrobial susceptibilities in Kobe, Japan and Taipei, Taiwan: an international analysis. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(2):e300060519867826. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060519867826
Lasserre JF, Brecx MC, Toma S. Oral microbes, biofilms and their role in periodontal and peri-implant diseases. Materials. 2018;11(10):e1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101802
Jamal M, Ahmad W, Andleeb S, et al. Bacterial biofilm and associated infections. J Chin Med Assoc. 2018;81(1):7–11. https://doi.org /10.1016/j.jcma.2017.07.012
Rajasekaran JJ, Krishnamurthy HK, Bosco J, et al. Oral microbiome: a review of its impact on oral and systemic health. Microorganisms. 2024;12(9):e1797. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/microorganisms12091797
Calhoun JH, Manring MM, Shirtliff M. Osteomyelitis of the long bones. Semin Plast Surg. 2009;23(2):59–72. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1214158
Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC. Robbins Basic Pathology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2012.
Brogden KA, Guthmiller JM, Taylor CE. Human polymicrobial infections. Lancet. 2005;365(9455):253–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(05)17745-9
Maisetta G, Batoni G. Editorial: interspecies interactions: effects on virulence and antimicrobial susceptibility of bacterial and fungal pathogens. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:e1922. https://doi.org/10. 3389/fmicb.2020.01922
Peters BM, Jabra-Rizk MA, O'May GA, Costerton JW, Shirtliff ME. Polymicrobial interactions: impact on pathogenesis and human disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012;25(1):193–213. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.00013-11
Limoli DH, Hoffman LR. Help, hinder, hide and harm: what can we learn from the interactions between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus during respiratory infections? Thorax. 2019;74(7):684–692. https://doi.org /10.1136/thoraxjnl-2018-212616
Khanolkar RA, Clark ST, Wang PW, et al. Ecological succession of polymicrobial communities in the cystic fibrosis airways. mSystems. 2020;5(6):e00809-20. https://doi.org/ 10.1128/mSystems.00809-20
Javed A, Manzoor S. Comparative analysis of bacterial vaginosis microbiota among pregnant and non-pregnant females and isolation of phages against enterococcus faecalis, enterococcus faecium, and shigella flexneri strains. Microb Pathog. 2020;149:e104588. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104588
Tomas M, Palmeira-de-Oliveira A, Simoes S, Martinez-de-Oliveira J, Palmeira-de-Oliveira R. Bacterial vaginosis: standard treatments and alternative strategies. Int J Pharm. 2020;587:e119659. https://doi.org /10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119659
Bair KL, Campagnari AA. Moraxella catarrhalis promotes stable polymicrobial biofilms with the major otopathogens. Front Microbiol. 2019;10:e3006. https://doi.org/ 10.3389/fmicb.2019.03006
Kaya E, Tollapi L, Pastore A, et al. Comparison of methods for the microbiological diagnosis of totally implantable venous access port-related infections. J Med Microbiol. 2020;69(11):1273–1284. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.001263
Azevedo AS, Almeida C, Melo LF, Azevedo NF. Impact of polymicrobial biofilms in catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2017;43(4):423–439. https://doi.org /10.1080/1040841x.2016.1240656
Sridhar S, Suprabha BS, Shenoy R, Suman E, Rao A. Association of streptococcus mutans, candida albicans and oral health practices with activity status of caries lesions among 5-year-old children with early childhood caries. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2020;18:911–919. https://doi.org/10.3290/j.ohpd.a45411
Škerk V, Schönwald S, Krhen I, et al. Aetiology of chronic prostatitis. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2002;19(6):471–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0924-8579(02)00087-0
Dahlen G, Basic A, Bylund J. Importance of virulence factors for the persistence of oral bacteria in the inflamed gingival crevice and in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. J Clin Med. 2019;8(9):e1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091339
Serra R, Grande R, Butrico L, et al. Chronic wound infections: the role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2015;13(5):605–613. https://doi.org/10.1586/14787210.2015.1023291
Tay WH, Chong KK, Kline KA. Polymicrobial-host interactions during infection. J Mol Biol. 2016;428(17):3355–3371. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.jmb.2016.05.006
Pierce EC, Dutton RJ. Putting microbial interactions back into community contexts. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2022;65:56–63. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.mib.2021.10.008
Karygianni L, Ren Z, Koo H, Thurnheer T. Biofilm matrixome:extracellular components in structured microbial communities. Trends Microbiol. 2020;28(8):668–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim. 2020.03.016
DeAntonio R, Yarzabal JP, Cruz JP, Schmidt JE, Kleijnen J. Epidemiology of otitis media in children from developing countries:a systematic review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;85:65–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.03.032
Schilder AG, Chonmaitree T, Cripps AW, et al. Otitis media. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2(1):e16063. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2016.63
Chonmaitree T, Trujillo R, Jennings K, et al. Acute otitis media and other complications of viral respiratory infection. Pediatr. 2016;137(4):e20153555. https://doi. org/10.1542/peds.2015-3555
Donlan RM, Costerton JW. Biofilms: survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002;15(2):167–193. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.15.2.167-193.2002
Jamal A, Alsabea A, Tarakmeh M, Safar A. Etiology, diagnosis, complications, and management of acute otitis media in children. Cureus. 2022;14(8):e28019. https://doi.org/ 10.7759/cureus.28019
Khairkar M, Deshmukh P, Maity H, Deotale V. Chronic suppurative otitis media: a comprehensive review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, microbiology, and complications. Cureus. 2023;15(8):e43729. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.43729
Elgharably H, Hussain ST, Shrestha NK, Blackstone EH, Pettersson GB. Current hypotheses in cardiac surgery: biofilm in infective endocarditis. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;28(1):56–59. https://doi.org /10.1053/j.semtcvs.2015.12.005
Linton MF, Yancey PG, Davies SS, et al. The Role of Lipids and Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis. Endotext; 2019.
Snow DE, Everett J, Mayer G, et al. The presence of biofilm structures in atherosclerotic plaques of arteries from legs amputated as a complication of diabetic foot ulcers. J Wound Care. 2016;25(Sup2):S16–S22. https://doi. org/10.12968/jowc.2016.25.Sup2.S16
Schrøder SA, Eickhardt S, Bjarnsholt T, Nørgaard T, Homøe P. Morphological evidence of biofilm in chronic obstructive sialadenitis. J Laryngol. Otol 2018;132(7):611-614. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215118000646
Kao WK, Chole RA, Ogden MA. Evidence of a microbial etiology for sialoliths. Laryngoscope. 2020;130(1):69–74. https://doi.org/ 10.1002/lary.27860
Crawford RW, Rosales-Reyes R, Ramirez-Aguilar MD, Chapa-Azuela O, Alpuche-Aranda C, Gunn JS. Gallstones play a significant role in Salmonella spp. gallbladder colonization and carriage. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2010;107(9):4353–4358. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1000862107
Dejea CM, Sears CL. Do biofilms confer a pro-carcinogenic state? Gut Microbes. 2016;7(1):54–57. https:// doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2015.1121363
Li S, Konstantinov SR, Smits R, Peppelenbosch MP. Bacterial biofilms in colorectal cancer initiation and progression. Trends Mol Med. 2017;23(1):18–30. https://doi.org /10.1016/j.molmed.2016.11.004
Diban F, Di Lodovico S, Di Fermo P, et al. Biofilms in chronic wound infections: innovative antimicrobial approaches using the in vitro lubbock chronic wound biofilm model. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):e1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021004
James GA, Swogger E, Wolcott R, et al. Biofilms in chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2008;16(1):37–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-475X.2007.00321.x
Jung H-S, Ehlers MM, Lombaard H, Redelinghuys MJ, Kock MM. Etiology of bacterial vaginosis and polymicrobial biofilm formation. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2017;43(6):651–667. https://doi.org/10.1080/1040841X.2017.1291579
Moreno I, Codoñer FM, Vilella F, et al. Evidence that the endometrial microbiota has an effect on implantation success or failure. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;215(6):684–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.ajog.2016.09.075
Douglas P. Re-thinking benign inflammation of the lactating breast: a mechanobiological model. Womens Health. 2022; 18: e17455065221075907. https://doi.org/ 10.1177/17455065221075907
Tan NC, Foreman A, Jardeleza C, Douglas R, Vreugde S, Wormald PJ. Intracellular staphylococcus aureus: the Trojan horse of recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis? Int Forum Allergy . 2013;3(4):261–266. https://doi.org /10.1002/alr.21154
Woo JH, Kim ST, Kang IG, Lee JH, Cha HE, Kim DY. Comparison of tonsillar biofilms between patients with recurrent tonsillitis and a control group. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2012;132(10):1115–1120. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2012.689859
Roberts AL, Connolly KL, Kirse DJ, et al. Detection of group a streptococcus in tonsils from pediatric patients reveals high rate of asymptomatic streptococcal carriage. BMC Pediatr. 2012;12(1):e3. https://doi.org /10.1186/1471-2431-12-3
Cattelan N, Dubey P, Arnal L, Yantorno OM, Deora R. Bordetella biofilms: a lifestyle leading to persistent infections. Pathog Dis. 2015;74(1):eftv108. https://doi.org/ 10.1093/femspd/ftv108
Hector A, Frey N, Hartl D. Update on host-pathogen interactions in cystic fibrosis lung disease. Mol Cell Pediatr. 2016;3(1):e12. https://doi.org/10.1186 /s40348-016-0039-5
Yoon BI, Han D-S, Ha US, et al. Clinical courses following acute bacterial prostatitis. Prostate Int. 2013;1(2):89–93. https://doi.org/10. 12954/PI.12013
Pendegast H, Leslie S, Rosario D. Chronic Prostatitis and Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome In Men. StatPearls; 2024.
Klein RD, Hultgren SJ. Urinary tract infections: microbial pathogenesis, host-pathogen interactions and new treatment strategies. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2020;18(4):211–226. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-020-0324-0
Copyright (c) 2025 Farah Liaqat, Waiza Ansar, Noor Muhammad, Maria Tariq, Zahid Nazir, Hafiz Muhammad Ghuffran Qamar, Iram Liaqat

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
BSR follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed the Copyright and Author Consent Form.










