Role of Rhizofungus (Aspergillus terreus) in Improving Biochemical and Physiologi-cal Parameters Affected by Lead Stress in Allium sativum L.
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
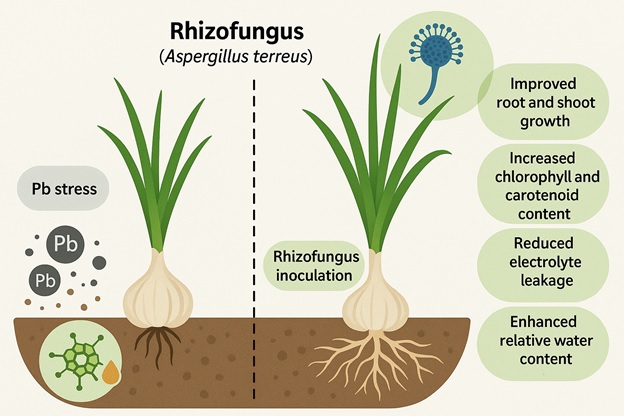
Background. Lead (Pb) contamination in agricultural soils is a growing concern, particularly in South and Southeast Asia, where root vegetables such as garlic and ginger are dietary staples. The primary sources of Pb in these regions include industrial discharge, mining activities, the excessive use of phosphate fertilizers, and atmospheric deposition. Pb disrupts plants’ physiological functions, that is, photosynthesis and nutrient uptake. It also enters the food chain, posing chronic health risks to human beings. Garlic (Allium sativum L.) is widely used for its culinary and medicinal value and remains especially susceptible to heavy metal accumulation in contaminated soils. This study investigates the potential of rhizospheric fungus (Aspergillus terreus) to mitigate Pb-induced stress in garlic, with a focus on enhancing agronomic traits and minimizing the health hazards associated with contaminated produce.
Method. Garlic plants were exposed to four treatment groups (control, rhizo-fungi alone, Pb stress (30 ppm), combined Pb stress (30 ppm) with rhizo-fungi inoculation). The experiment followed a randomized complete block design (RCBD) with three replicates per treatment.
Results. Pb exposure led to significant reductions in physiological parameters, including root and shoot length, fresh and dry weight, seed germination, and relative water content (RWC). Electrolyte leakage increased under Pb stress, indicating membrane damage. However, co-application of rhizo-fungi improved these physiological traits, that is, 18% increase in shoot length, 20% improvement in RWC, and 15% reduction in electrolyte leakage, as compared to Pb-treated plants. Biochemical analysis revealed a decline in cholorphyll and carotenoid levels under Pb stress, while rhizo-fungi inoculation enhanced the chlorophyll content by 25%, confirming its role in restoring photosynthetic efficiency.
Conclusion. This study highlights the potential of symbiotic rhizo-fungi to mitigate Pb stress in garlic, improving both growth and biochemical parameters. The findings suggest that rhizo-fungi is an effective bio-remediating agent, enhancing crop resilience in contaminated soils.
Downloads
References
Zahoor M, Irshad M, Rahman H, et al. Alleviation of heavy metal toxicity and phytostimulation of Brassica campestris L. by endophytic Mucor sp. MHR-7. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2017;142:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.04.005
Husna, Hussain A, Shah M, Hamayun M, Qadir M, Iqbal A. Heavy metal tolerant endophytic fungi Aspergillus welwitschiae improves growth, ceasing metal uptake and strengthening antioxidant system in Glycine max L. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2021;29:15501–15515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16640-1
Husna el al. demonstrated that this study is of special importance as it demonstrates how endophytic fungi reduce metal uptake and boost plant defense systems, directly supporting the concept of fungal-assisted phytoremediation.
Sarker B, Keya KN, Mahir FI, Nahiun KM, Shahida S, Khan RA. Surface and ground water pollution: causes and effects of urbanization and industrialization in South Asia. Sci Rev. 2021;7(3):32–41. https://doi.org/10.32861/sr.73.32.41
Kefale B, Delele MA, Fanta SW, Abate SM. Nutritional, physicochemical, functional, and textural properties of red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.), red onion (Allium cepa), ginger (Zingiber officinale), and garlic (Allium sativum): Main ingredients for the preparation of spicy foods in Ethiopia. J Food Qual. 2023;2023(1):e3916692. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/3916692
Collin MS, Venkatraman SK, Vijayakumar N, et al. Bioaccumulation of lead (Pb) and its effects on human: a review. J Hazard Mater Adv. 2022;7:e100094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2022.100094
Qadir M, Hussain A, Shah M, et al. Comparative assessment of chromate bioremediation potential of Pantoea conspicua and Aspergillus niger. J Hazard Mater. 2022;424:e127314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127314
Shah N, Qadir M, Irshad M, et al. Enhancement of cadmium phytoremediation potential of Helianthus annuus L. with application of EDTA and IAA. Metabolites. 2022;12(11):e1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111049
Qadir et al. exlained the synergistic role of chelators and phytohormones in enhancing phytoremediation, offering mechanistic insights for metal detoxification strategies.
Ikram M, Ali N, Jan G, et al. IAA producing fungal endophyte Penicillium roqueforti Thom., enhances stress tolerance and nutrient uptake in wheat plants grown on heavy metal contaminated soils. PLoS One. 2018;13(11):e0208150. https://doi.org /10.1371/journal.pone.0208150
Bilal L, Asaf S, Hamayun M, et al. Plant growth promoting endophytic fungi Aspergillus fumigatus TS1 and Fusarium proliferatum BRL1 produce gibberellins and regulate plant endogenous hormones. Symbiosis. 2018;76:117–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-018-0545-4
Zhang H, Xu Z, Guo K, et al. Toxic effects of heavy metal Cd and Zn on chlorophyll, carotenoid metabolism and photosynthetic function in tobacco leaves revealed by physiological and proteomics analysis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020;202:e110856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110856
Ali I, Hussain J, Yanwisetpakdee B, Iqbal I, Chen X. The effects of monoculture and intercropping on photosynthesis performance correlated with growth of garlic and perennial ryegrass response to different heavy metals. BMC Plant Biol. 2024;24(1):e659. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-024-05371-3
Hundare A, Joshi V, Joshi N. Salicylic acid attenuates salinity-induced growth inhibition in in vitro raised ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) plantlets by regulating ionic balance and antioxidative system. Plant Stress. 2022;4:e100070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stress.2022.100070
Sravya MVN, Simhachalam G, Kumar NS, Govindarao K, Sandeep TR, Divya D. Anti-pathogenicity of Acanthus ilicifolius leaf extracts against A. hydrophila infection in Labeo rohita fingerlings. AMB Express. 2023;13(1):e86. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-023-01595-y
Zygielbaum AI, Gitelson AA, Arkebauer TJ, Rundquist DC. Non-destructive detection of water stress and estimation of relative water content in maize. Geophys Res Lett. 2009;36(12):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL038906
Dilawar N, Hamayun M, Iqbal A, et al. Rhizofungus Aspergillus terreus mitigates heavy metal stress-associated damage in Triticum aestivum L. Plants. 2024;13(18):e2643. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13182643
Dilawar et al. provided direct evidence of A. terreus in reducing Pb and Cu stress in wheat in their paper, making it a critical reference for fungal bioremediation research.
Khan A, Ali S, Khan M, Hamayun M, Moon YS. Parthenium hysterophorus’s endophytes: the second layer of defense against biotic and abiotic stresses. Microorganisms. 2022;10(11):e2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112217
Dilawar N, Asad F, Shahid S. Role of hydroxyl benzoic acid foliar spray on amelioration of lead tolerance on Triticum aestivum L. Pure Appl Biol. 2021;10(3):861–871. https://doi.org/ 10.19045/bspab.2021.100088
Mehmood A, Hussain A, Irshad M, Hamayun M, Iqbal A, Khan N. In vitro production of IAA by endophytic fungus Aspergillus awamori and its growth promoting activities in Zea mays. Symbiosis. 2019;77:225–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-018-0583-y
Demidchik V, Shabala SN, Outts KB, Tester MA, Davies JM. Free oxygen radicals regulate plasma membrane Ca2+- and K+-permeable channels in plant root cells. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.00201
Demidchik V, Straltsova D, Medvedev SS, Pozhvanov GA, Sokolik A, Yurin V. Stress-induced electrolyte leakage, the role of K+ permeable channels and involvement in programmed cell death and metabolic adjustment. J Exp Bot. 2014;65:1259–1270. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru004
Ahmad P, Allah EA, Hashem A, Sarwat M, Gucel S. Exogenous application of selenium mitigates cadmium toxicity in Brassica juncea L. (Czern & Cross) by upregulating antioxidative system and secondary metabolites. J Plant Growth Regul. 2016;35:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-016-9592-3
Their study is of outstanding importance as it provides a model of how exogenous treatments enhance antioxidative responses under metal stress, reinforcing the biochemical basis of plant stress physiology.
Ahmad P, Ahanger MA, Alyemeni MN, Wijaya L, Alam P. Exogenous application of nitric oxide modulates osmolyte metabolism, antioxidants, enzymes of ascorbate-glutathione cycle and promotes growth under cadmium stress in tomato. Protoplasma. 2018;255:79–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1132-x
RunHong M, Cheng J, Tang F, Yue J, Li Z, Ni Z. Heavy metals in bamboo shoots from Southeastern China and risk assessment. Food Addit Contam Part B. 2021;14:264–270. https://doi.org/10.1080/19393210.2021.1947900
Hasanuzzaman M, Fujita M. Exogenous sodium nitroprusside alleviates arsenic-induced oxidative stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings by enhancing antioxidant defense and glyoxalase system. Ecotoxicology. 2013;22:584–596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1050-4
Copyright (c) 2025 Naveen Dilawar, Muhammad Saifullah, Attaur Rahman, Azaz Ahmad, Muhammad Usman, Muhammad Nawaz

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
BSR follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed the Copyright and Author Consent Form.










