HPLC-Based Elucidation of Tannins from the Tissue and Callus Culture Extracts of Selected Medicinal Plants
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
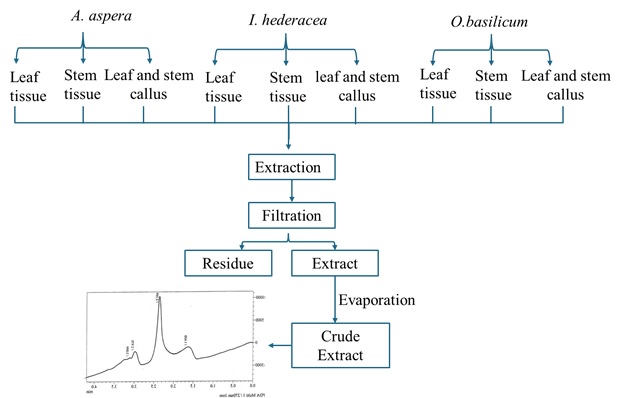
Background. Optimized HPLC profiling is a powerful and effective analytical tool to standardize plant samples and authenticate plant materials. In this study, three selected medicinal plants namely: Achyranthes aspera, Ipomoea hederacea, and Ocimum basilicum were subjected to callus induction following seedling, leaf, and stem germination.
Methods. The induced callus was subsequently dried, finely ground, and extracted using methanol and water for HPLC analysis. A validated procedure was employed to identify and separate the tannin content in seedling leaf, stem, and callus culture extracts. HPLC fingerprinting was performed using a Shimadzu LC-20A system with a retention time of 2.9 minutes at 270 nm. The aim was to ensure quality and consistency in tannin analysis across different plant parts and callus culture samples.
Results. The highest callogenic response occurred in A. aspera leaf explants on MS medium with 2.0 mg/L 2,4-D and 4.0 mg/L NAA, producing green, granular callus. The lowest was in I. hederacea stem explants with 0.5 mg/L 2,4-D and BAP, yielding brown, granular callus. O. basilicum leaf callus extract showed the largest sample area (9365.56) and tannin content (2.66), with superior precision in tannin analysis for O. basilicum and A. aspera (7.81).
Conclusion. HPLC profiling proved to be an accurate, efficient, and precise method for evaluating tannin content in selected plant samples. It is a crucial method to standardize the quality of medicinal plant compounds.
Downloads
References
Steward FC, Mapes MO, Mears K. Growth and organized development of cultured cells. II. Organization in cultures grown from freely suspended cells. Am J Bot. 1958;45(9):705–708. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.15372197.1958.tb10599.x
Steward et al. demonstrated that freely suspended plant cells in culture can develop organized structures, highlighting the totipotency of plant cells. This study laid foundational work for modern plant tissue culture and regeneration techniques.
Sen MK, Nasrin S, Rahman S, Jamal AHM. In vitro callus induction and plantlet regeneration of Achyranthes aspera L., a high value medicinal plant. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2014;4(1):40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/S22211691(14)60206-9
Sen et al. optimized in vitro protocols for callus induction and plantlet regeneration of Achyranthes aspera, a medicinally important plant. Their findings support conservation and large-scale propagation through tissue culture techniques.
Haliński LP, Szafranek J, Szafranek BM, Gołębiowski M, Stepnowski P. Chromatographic fractionation and analysis of the main components of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) leaf cuticular waxes. Acta Chromatograph. 2009;21(1):127–137. https://doi.org/10.1556/AChrom.21.2009.1.11
Haliński et al. analyzed the chemical composition of cuticular waxes from Solanum melongena leaves using chromatographic techniques. Their study identified major wax components, contributing to the understanding of plant surface chemistry and defense.
Tiwari S, Bhadoriya U, Saini L, Gupta A, Solanki S. Quantitative analysis of glycyrrhizic acid by HPTLC in herbal formulation. Asian J Pharmaceut Life Sci. 2011;1(2):124–127.
Tiwari et al. performed quantitative analysis of glycyrrhizic acid in herbal formulations using High-Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC). The study ensured quality control and standardization of herbal products containing Glycyrrhiza glabra.
Winiarska-Mieczan A, Muszyński S, Tomaszewska E, et al. The impact of tannic acid consumption on bone mineralization. Metabolites. 2023;13(10):e1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13101072
Winiarska-Mieczan et al. investigated the effects of tannic acid consumption on bone mineralization. Their findings revealed that excessive intake may negatively influence bone health, highlighting potential dietary risks.
Choubey S, Goyal S, Varughese L, Kumar V. Probing gallic acid for its broad-spectrum applications. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018;18(15):1283–1293. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557518666180330114010
Choubey et al. reviewed the diverse pharmacological applications of gallic acid, emphasizing its antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anticancer properties. The study highlights its potential as a multifunctional bioactive compound in medicinal chemistry.
Chung KT, Wong TY, Wei CI, Huang YW, Lin Y. Tannins and human health: a review. Critical Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1998;38(6):421–464. https:// doi.org/10.1080/10408699891274273
Chung et al. provided a comprehensive review on tannins, discussing their sources, biological activities, and effects on human health. The study highlighted both beneficial and adverse impacts, depending on dosage and dietary context.
Banerjee KGJ, Gupta AK, Daha P. Phytochemical constituents and pharmacological uses of medicinal plant Achyranthes aspera: a review. World J Pharmaceut Res. 2015;4(1):470–489.
Banerjee et al. reviewed the phytochemical profile and pharmacological activities of Achyranthes aspera, emphasizing its therapeutic potential. The study compiles traditional and modern uses, supporting its role in herbal medicine.
Shashikanth J, Dorcas M, Mugendhiran S, Renu. Biodiversity with special reference to indigenous systems of medicinal plants, ornamental and weeds of University College for Women, Koti, Osmania University, Hyderabad, Telangana, India. Ann Plant Sci. 2023;12(10):5976–6032. https://doi. org/10.21746/aps.2023.12.10.1
Shashikanth et al. documented the biodiversity of medicinal, ornamental, and weed plant species at University College for Women, Osmania University. The study emphasizes the importance of indigenous plant systems for conservation and sustainable use.
Ambreen M, Mirza SA, Bano Z, et al. Antioxidant and anticancer activity of tannins isolated from callus cultures of Achyranthes aspera L. Sci Inq Rev. 2024;8(2):1–21. https://doi.org/10.32350/sir.82.01
Ambreen et al. evaluated tannins extracted from Achyranthes aspera callus cultures for their antioxidant and anticancer properties. The study demonstrated significant bioactivity, supporting their potential use in therapeutic applications.
Haq MZU, Riaz M, De Feo V. Ipomea hederacea Jacq.: a medicinal herb with promising health benefits. Molecules. 2012;17(11):13132–13145. https:// doi.org/10.3390/molecules171113132
Haq et al. reviewed the medicinal properties of Ipomoea hederacea, highlighting its phytochemical composition and potential therapeutic benefits. The study supports its traditional use and encourages further pharmacological research.
Awan ZI, Habib-ur-Rehman A, Awan A, Minhas FA, Khan MN. Ethnobotanical importance of some highly medicinal plants of District Muzaffarabad, Pakistan with special reference to the species of the genus Viburnum. J Pharm Biol Sci. 2013;6(2):53–66. https://doi.org/10.9790/3008-0625366
Awan et al. explored the ethnobotanical significance of medicinal plants in Muzaffarabad, Pakistan. The study highlights traditional knowledge and the therapeutic potential of these plants for local healthcare.
Tanveer H, Safdar A, Asi MR. Appraisal of an important flavonoid, quercetin, in callus cultures of Citrullus colocynthis. Int J Agric Biol. 2012;14(4):1814–9596.
Tanveer et al. assessed the presence of quercetin, a valuable flavonoid, in callus cultures of Citrullus colocynthis. The study underscores the potential of in vitro cultures for producing bioactive compounds with medicinal value
Al-Askar AAI, Bashir S, Abdallah E, et al. Antimicrobial efficacy and HPLC analysis of polyphenolic compounds in a whole-plant extract of Eryngium campestre. Separations. 2023;10(6):e362. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060362
Al-Askar et al. investigated the antimicrobial activity and polyphenolic profile of whole-plant extracts of Eryngium campestre using HPLC. The study revealed strong antimicrobial efficacy, highlighting its potential in natural therapeutics.
Senthilmanickam J, Bhavani AL, Venkatramlingam K, Chandra G. The role of 2,4-D and NAA in callus induction of Achyranthes aspera and its secondary metabolite studies. J Appl Nat Sci Online. 2012;2(3):232–243.
Senthilmanickam et al. examined the effects of 2,4-D and NAA on callus induction in Achyranthes aspera and analyzed its secondary metabolites. The study demonstrated hormone-specific responses influencing callus formation and bioactive compound production.
Kayani S, Zia M, Sarwar S, Chaudhary MF. Callogenic studies of Achyranthes aspera leaf explant at different hormonal combinations. Pak J Biol Sci. 2008;11(6):950–952. https://doi. org/10.3923/pjbs.2008.950.952
Kayani et al. investigated callus induction in Achyranthes aspera leaf explants using various hormonal combinations. The study identified optimal conditions for callogenesis, aiding in tissue culture-based propagation of the species.
World Health Organization. The Selection of Essential Drugs. Second Report of the WHO Expert Committee. World Health Organization; 1979.
WHO published the second report on the selection of essential drugs, outlining criteria for prioritizing medicines based on public health relevance, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness. This report laid the groundwork for national essential medicines lists worldwide.
Edeoga HO, Okwu DE, Mbaebie BO. Phytochemical constituents of some Nigerian medicinal plants. Afr J Biotechnol. 2005;4(7):685–688. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB2005.000-3127
Edeoga et al. analyzed the phytochemical constituents of selected Nigerian medicinal plants, identifying key compounds like alkaloids, flavonoids, and tannins. The study supports the therapeutic potential of these plants in traditional medicine.
Kpoviéssi DSS, Gbaguidi F, Gbénou J, et al. Validation of a method for the determination of sterols and triterpenes in the aerial part of Justicia anselliana (Nees) T. Anders by capillary gas chromatography. J Pharmaceut Biomed Anal. 2008;48(4):1127–1135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2008.08.036
Kpoviéssi et al. validated a capillary gas chromatography method for analyzing sterols and triterpenes in the aerial parts of Justicia anselliana. The study ensures accurate phytochemical profiling for quality control in herbal formulations.
Faiyazuddin MDA, Rauf N, Ahmad. A validated HPTLC method for determination of terbutaline sulfate in biological samples: application to pharmacokinetic study. Saudi Pharmaceut J. 2011;19(3):185–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2011.03.004
Faiyazuddin et al. developed and validated an HPTLC method for detecting terbutaline sulfate in biological samples. The method was successfully applied in pharmacokinetic studies, offering a reliable tool for drug monitoring.
Ahmed R. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): principles, applications, versatility, efficiency, innovation and comparative analysis in modern analytical chemistry and in pharmaceutical sciences. Clinic Invest. 2024;14(9):524–535. https://doi.org/ 10.20944/preprints202409.0057.v1
Ahmed provided an in-depth overview of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), highlighting its principles, efficiency, and wide-ranging applications in analytical chemistry and pharmaceutical sciences. The study emphasizes HPLC's innovation and versatility in modern research.
Durgawale TP, Durgawale PP, Khanwelkar CC. Quantitative estimation of tannin by HPLC. Der Pharm Lett. 2016;8(3):123–126.
Durgawale et al. conducted quantitative estimation of tannins using HPLC, demonstrating an accurate and efficient method for tannin analysis. The study supports its application in standardizing tannin-rich herbal formulations.
Mradu GS, Saumyakanti, Sohini M, Arup M. HPLC profiles of standard phenolic compounds present in medicinal plants. Int J Pharm Phytochem Res. 2012;4(3):162–167.
Mradu et al. presented HPLC profiles of standard phenolic compounds in various medicinal plants, enabling accurate identification and quantification. The study aids in quality control and validation of plant-based formulations.
Obafemi TO, Akinmoladun AC, Olaleye MT, et al. High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) fingerprinting, mineral composition and in vitro antioxidant activity of methanol leaf extract of Synsepalum dulcificum (Sapotaceae). J Appl Pharmaceut Sci. 2017;7(10):125–131.
Obafemi et al. performed HPLC fingerprinting and mineral analysis of Synsepalum dulcificum leaf extract, revealing significant antioxidant activity. The study supports its pharmacological potential and use in herbal medicine.
Ruiz-Aquino F, Feria-Reyes R, Rutiaga-Quiñones JG, Robledo-Taboada LH, Gabriel-Parra R. Characterization of tannin extracts derived from the bark of four tree species by HPLC and FTIR. Forest Sci Technol. 2023;19(1):38–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/21580103.2023.2166593
Ruiz-Aquino et al. characterized tannin extracts from the bark of four tree species using HPLC and FTIR techniques. Their findings provided detailed insights into the chemical composition and potential applications of these natural extracts.
Rathod ZR, Sarita S, Saraf MS. Identification and estimation of total tannins from Citrus limon L. Burm. f. (lemon) and its endophytes. Curr Trends Biomed Eng Biosci. 2022;20(5):1–12.
Rathod et al. identified and quantified total tannins from Citrus limon and its associated endophytes. The study highlights the role of endophytes in enhancing bioactive compound production for potential therapeutic applications.
Copyright (c) 2025 Madieha Ambreen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
BSR follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed the Copyright and Author Consent Form.










