Developing Urdu Stories to Address Articulation Errors in Children
Abstract
 Abstract Views: 0
Abstract Views: 0
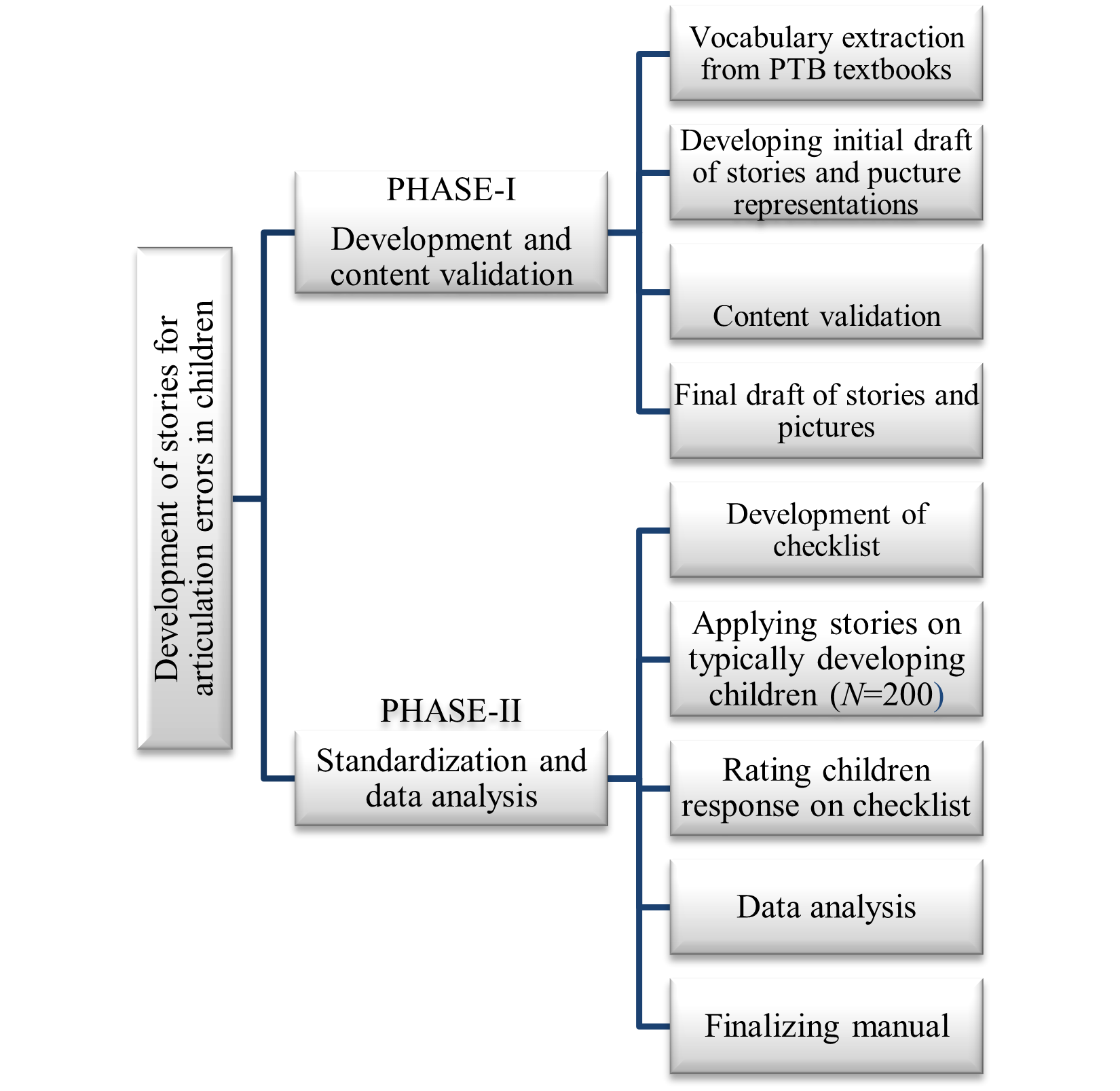
The recent study centered on the development and standardization of Urdu stories as an intervention tool to address articulation errors. A mixed method design was employed, consisting of two phases. Phase I utilized qualitative methods, focused on story development and content validation, while Phase II used quantitative method and involved standardization and data analysis. Stories were developed by compiling age appropriate vocabulary from PTB (Punjab Textbook Board) books for the targeted sounds /g/, /k/, /chh/, /kh/ and /ph/ at initial, middle and final position of the word in Urdu language. Additionally, pictures of the stories were developed. For content validation, even speech and language pathologists and three Urdu language experts were consulted. The feedback obtained from these experts was then integrated into the stories and pictures to finalize them. Content validity was assessed through I-CVI, with scores ranging from 0.8 to 1, indicating high level of agreement among experts. In the second phase the finalized stories were applied on the sample of 200 typically developing Urdu speaking children within the age range of 3 to 7 years. Sample was selected through purposive sampling. The Cronbach’s alpha value ranging from 0.93-0.98>0.78 indicated high internal consistency. The mean score of Item’s difficulty lie within the range of 3.00 to 5.00. Results revealed that the developed stories were reliable and age appropriate and can be used as an intervention tool to address articulation errors in Urdu-speaking children.
Downloads
References
Ahmadi, A., Kamali, M., Mohamadi, R., Zarifian, T., Ebadi, A., Kazemi, M. T., & Ghasisin, L. (2019). Assessment of speech sound production by story-retelling in Persian-speaking children: Introducing a new instrument. Iranian Journal of Medical Sciences, 44(4), 299–306. https://doi.org/10.30476/ijms.2019.44956
Altoeriqi, E., & Aljutaily, M. (2023). Covert contrast in acquiring fricatives by preschool children: Evidence from Najdi Arabic. SAGE Open, 13(4), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440231211688
Ambreen, S., & To, C. K. S. (2021). Phonological development in Urdu-speaking children: A systematic review. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 64(11), 4213–4234. https://doi.org/10.1044/2021_jslhr-21-00148
Aslam, I., Mumtaz, N., & Saqulain, G. (2020). Prevalence of speech sound disorders among primary school children. Journal of Islamabad Medical and Dental College, 9(3), 195–200. https://doi.org/10.35787/jimdc.v9i3.283
Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory. Prentice hall.
Cabbage, K. L., & DeVeney, S. L. (2020). Treatment approach considerations for children with speech sound disorders in school-based settings. Topics in Language Disorders, 40(4), 312–325. https://doi.org/10.1097/tld.0000000000000229
Denissen, J. J., Soto, C. J., Geenen, R., John, O. P., & Van Aken, M. A. (2022). Matters arising from Lee et al. (2022). Personality and Individual Differences, 199, Article e111838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2022.111838
Freeman, J. B. (2016). Speaking of stories: An exploration of oral stories as an intervention in speech sound disorders. Storytelling, Self, Society, 12(2), 207–247. https://doi.org/10.13110/storselfsoci.12.2.0207
Furlong, L. M., Morris, M. E., Serry, T. A., & Erickson, S. (2021). Treating childhood speech sound disorders: Current approaches to management by Australian speech-language pathologists. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 52(2), 581–596. https://doi.org/10.1044/2020_lshss-20-00092
Hessling, A., & Schuele, C. M. (2020). Individualized narrative intervention for school-age children with specific language impairment. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 51(3), 687–705. https://doi.org/10.1044/2019_lshss-19-00082
Hustad, K. C., Mahr, T. J., Natzke, P., & Rathouz, P. J. (2021). Speech development between 30 and 119 months in typical children I: Intelligibility growth curves for single-word and multiword productions. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 64(10), 3707–3719. https://doi.org/10.1044/2021_JSLHR-21-00142
Kairienė, D. (2017). The motor learning approach and strategies in the treatment of children’s articulation disorders. Specialusis Ugdymas, 1(36), 117–152. https://doi.org/10.21277/se.v1i36.28
Khan, M. S. G., Noreen, H., & Khan, M. A. (2021). Effectiveness of linguistic base approach and traditional articulation therapy to improve articulation among children (8-12 years) with mild to severe hearing loss. Journal of Rehman Medical Institute, 7(1), 8–12.
Kyriazos, T. A., & Stalikas, A. (2018). Applied psychometrics: The steps of scale development and standardization process. Psychology, 9(11), 2531–2560. https://doi.org/10.4236/psych.2018.911145
Loudermill, C., Greenwell, T., & Brosseau-Lapré, F. (2021). A comprehensive treatment approach to address speech production and literacy skills in school-age children with speech sound disorders. Seminars in Speech and Language, 42(2), 136–146. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1723840
Macchi, L., Schelstraete, M., Ané, C., Boidein, F., Riquet, A., & Casalis, S. (2024). Predictive factors of reading in children with developmental language disorder. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 247, Article e106042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2024.106042
Naz, A., Noor, H. S., Hussain, A., Bukhari, S. A., Pervaiz, N., & Inam, I. (2023). Comparison of traditional articulation therapy and picture articulation test in children with articulation disorders. Journal of Health and Rehabilitation Research, 3(2), 448–453. https://doi.org/10.61919/jhrr.v3i2.139
Nayeb, L., Lagerberg, D., Sarkadi, A., Salameh, E., & Eriksson, M. (2020). Identifying language disorder in bilingual children aged 2.5 years requires screening in both languages. Acta Paediatrica, 110(1), 265–272. https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.15343
Otasevic, J., Vukasinovic-Radojicic, Z., & Otasevic, B. (2021). Correlation of neuropsychological indicators of child development with speech: Empirical research underpinning the National Children’s Health Prevention Programme. Vojnosanitetski Pregled, 79(7), 673–680. https://doi.org/10.2298/vsp210205032o
Palumbo, M. L., Mody, M., Klykylo, W. M., Ballard, K. J., McDougle, C. J., & Guenther, F. H. (2024). Neurodevelopmental disorders: Speech and language disorders. In A. Tasman, M. B. Riba, R. D. Alarcón, C. A. Alfonso, S. Kanba, D. Lecic-Tosevski, D. M. Ndetei, C. H. Ng, & T. G. Schulze (Eds.), Tasman’s Psychiatry (pp. 1533–1559). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51366-5_86
Rinaldi, S., Caselli, M. C., Cofelice, V., D’Amico, S., De Cagno, A. G., Della Corte, G., Di Martino, M. V., Di Costanzo, B., Levorato, M. C., Penge, R., Rossetto, T., Sansavini, A., Vecchi, S., & Zoccolotti, P. (2021). Efficacy of the treatment of developmental language disorder: A systematic review. Brain Sciences, 11(3), Article e407. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030407
Spencer, T. D., & Petersen, D. B. (2020). Narrative intervention: Principles to practice. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 51(4), 1081–1096. https://doi.org/10.1044/2020_lshss-20-00015
Thomas, N., Colin, C., & Leybaert, J. (2020). Interactive reading to improve language and emergent literacy skills of preschool children from low socioeconomic and language-minority backgrounds. Early Childhood Education Journal, 48(5), 549–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-020-01022-y
Yusoff, M. S. B. (2019). ABC of content validation and content validity index calculation. Education in Medicine Journal, 11(2), 49–54. https://doi.org/10.21315/eimj2019.11.2.6

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
UER follows an open-access publishing policy and full text of all published articles is available free, immediately upon publication of an issue. The journal’s contents are published and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY 4.0) license. Thus, the work submitted to the journal implies that it is original, unpublished work of the authors (neither published previously nor accepted/under consideration for publication elsewhere). On acceptance of a manuscript for publication, a corresponding author on the behalf of all co-authors of the manuscript will sign and submit a completed Copyright and Author Consent Form.
Copyright (c) The Authors









